Since its inception Reserve Bank has
been playing key role in the formulation of monetary, banking and financial
policies. No Department has witnessed the various phases of transition of Indian
banking system from a closed one to well-liberalized one (particularly since
mid-1990s) from closer quarters than the Department of Banking Operations and
Development - popularly called DBOD. To facilitate the transition
process and in order to effectively perform its varying roles in the changing
banking scenario, from regulator to facilitator over the period, Department
has undergone various organizational changes and so also in its activities,
approach and functioning.
2. As varied segments within and
without RBI interact with the Department on banking and related issues/matters,
we brought out a handbook of information on the Department aptly christened as
" This is. DBOD" in February 2004 on the changing face of the Department
for their information and benefit. The handbook was placed on RBIs website and
widely covered in Banks Newsletter. Encouraging response coupled with certain
important organizational developments has necessitated the revision and updation
of first edition.
3. The handbooks language and style of
presentation is in keeping in view the interests of our cross-section of readers
and users, whether our other departments / Offices, colleagues, bankers,
academicians or others. We hope that they would find it a useful publication for
the intended purpose and enrich it with their valuable suggestions.
4. The contributions of our colleagues
to the publication are immensely appreciated and gratefully
acknowledged.
Reserve Bank of India (
C.R.Muralidharan)
Department of Banking
Operations Chief General Manager-in-Charge &
Development
Central Office
Mumbai
September 30, 2004
Reserve Bank of India has been
empowered under Banking Regulation Act, 1949 to conduct the inspection of banks
and regulate them in the interest of banking system, banking policy and
depositors/public. While the Department of Banking Operations and Development
exercises regulatory powers in respect of commercial banks and Local Area Banks
(LABs), Regional Rural Banks/District and State Co-operative Banks and Urban
Co-operative Banks are regulated by Rural Planning and Credit Department and
Urban Banks Department, respectively.
The Department of Banking Operations
and Development is entrusted with the responsibility of regulation of commercial
banks and LABs under the regulatory provisions contained in the Banking
Regulation Act, 1949 and the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and other related
statutes besides enunciation of banking polices. It's functions broadly relate
to prescription of regulations for compliance with various provisions of Banking
Regulation Act on establishment of banks such as licensing and branch expansion,
maintenance of statutory liquidity reserves, management and operations,
amalgamation, reconstruction and liquidation of banking companies. The other
important activities of the Department include approval for setting up of
subsidiaries and undertaking of new activities by commercial banks. The
Department endeavours towards promoting and fostering a sound, multi-faceted and
competitive banking system by laying down norms for prudential regulation of
commercial banks. It is also responsible for putting in place a pro-active
environment for development of new products and consequently, the Department has
to keep itself abreast of developments domestically and globally and formulate
policy responses accordingly by suggesting amendments to the existing
laws/enactment of new legislation, regulation etc. Concomitant with the above
statutory obligation enjoined on it, the Department strives to bring the
regulatory standards of commercial banks on par with the international best
practices. In order to achieve its objective of establishing a world class
banking system in India, it has to maintain professionally skilled staff in a
flexible organizational set-up with activities in tune with the
time.
2. The handbook provides basic
information about the Department through two sections, viz.
Section - I : Organizational
set-up
Section - II : Major activities of
various Sections/Cells
Section - I briefly throws light
on the organizational set-up of the Department reflecting its various functional
groups with their allocations under respective Chief General Managers. The
statistical and other information furnished therein is as on September 1, 2004
and is subject to changes.
Section - II describes the major
activities of individual Sections/Cells of the Department in a brief manner.
Besides those activities, these Sections/Cells contribute material for Reserve
Banks publications like Annual Report, Report on Trend and Progress of Banking
in India, Report on Currency and Finance, publications of Government of India /
International Organizations. They take follow-up action on points emanating from
meetings of Board for Financial Supervision (BFS), Central / Local Board of
Directors and reports of various Committees / Working Groups. They also attend
to related Parliament questions, legal matters, court cases, references from
governments, trade bodies, public etc. The Department also brings out every
month a report on its important activities and submits half- yearly /yearly
reports for Board for Financial Supervision (BFS) and an annual report to the
Central Board of Directors. It places its bank circulars (including Master
Circulars) and Frequently Asked Questions publication on RBI website for the
benefit of bankers and others. The Master Circulars are periodically updated /
revised. The Department is also represented in various Committees, Working
Groups, Forums etc. of RBI, banks, governments, etc. The intranet site of the
Department which was launched on April 20, 2004 contains comprehensive
information relating to its functions and working, bank circulars, monthly
report on the important activities of the Department, Banks publications,
banking statutes, etc.
3. The Department functions in an
environment supportive of consultative decision-making process. Important
policies are decided keeping in view the best international practices,
views/comments from the regulated entities, academia and other market
participants.
The Department has pyramid - pattern
organisational set-up. It is headed by Chief General Manager-in-Charge, and has
three other Chief General Managers. Besides, there are 22 Senior Officers viz. 8
General Managers and 14 Deputy General Managers. They look after their
respective portfolios as shown in the chart. The working strength of the
Department as on September 1, 2004 is as under: Officers-110, Class III
employees 107 and Class IV employees 77.
2. The Department comprises 19 Sections
/ Cells which attend to their respective areas of work, viz. Anti-Money
Laundering Cell, Appointments Section, Branch Licensing Section, Banking Policy
Section, Computer & Technology Cell, Directives Section, Defaulters List
Cell, Financial Services Cell, International Banking Section, Information
Section, Industrial and Export Credit Section, JPC Cell, Legislation Section,
Private Sector Banks Section, Parliament Cell, Reconstruction Section, Returns
Section, Rajbhasha Anubhag and Administration & Establishment Division.
3. The major activities of the above
Sections/Cells have been described in Section - II. Pursuant to the
recommendations of the High Level Review Group constituted by RBI in July 2002,
the Department has since taken over the responsibility of regulating Local Area
Banks from Rural Planning and Credit Department. Following the recommendations
of the Committee on Job Consolidation / Re-alignment, the Regional Offices (ROs)
of the Department excepting Mumbai Regional Office (MRO) were merged with
Regional Offices of Department of Banking Supervision (DBS) with effect from May
10, 2004. MRO was merged with DBOD, CO in the interest of operational
expediency; consequently, its certain activities are being attended to by
Central Office. Further, the activities of erstwhile Industrial and Export
Credit Department relating industrial credit policy, export credit policy and
industrial rehabilitation were merged with DBOD, CO for better synergy with
effect from July 1, 2004.
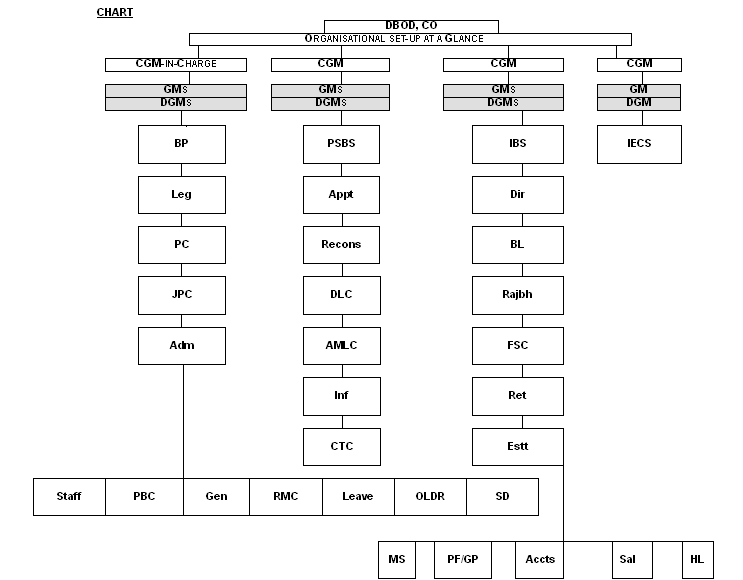
Notes: (1) The abbreviations
'CGM', 'GM' and 'DGM' stand for Chief General Manager, General Manager and
Deputy General Manager, respectively.
(2) The list of other abbreviations is
given below:
Accts --- Accounts Section
Adm --- Administration
Division
AMLC --- Anti-Money Laundering
Cell
Appt --- Appointments
Section
BL --- Branch Licensing
Section
BP --- Banking Policy
Section
CTC --- Computer & Technology
Cell
Dir --- Directives Section
DLC --- Defaulter Lists Cell
Estt --- Establishment
Division
FSC --- Financial Services
Cell
Gen --- General Section
HL --- Housing Loan Section
IBS --- International Banking
Section
Inf --- Information Section
IECS --- Industrial & Export Credit
Section
JPC --- Joint Parliamentary Committee
Cell
Leave --- Leave Section
MS --- Medical Section
Leg --- Legislation Section
OLDR --- Officers' Lounge & Dining
Room
PC --- Parliament Cell
PBC --- Planning & Budget
Cell
PSBS --- Private Sector Banks
Section
PF / GP --- Provident Fund, Gratuity,
Pension Cell
Recons --- Reconstruction
Section
Ret --- Returns Section
RMC --- Records Management
Cell
Rajbh --- Rajbhasha Anubhag
SD --- Staff Dispensary
Staff --- Staff Section - I, II,
III
Sal --- Salary
Section
- Anti-Money Laundering Cell
- Appointments Section
- Branch Licensing Section
- Banking Policy Section
- Computer & Technology Cell
- Directives Section
- Defaulter Lists Cell
- Financial Services Cell
- International Banking Section
- Information Section
- Industrial and Export Credit Section
- JPC Cell
- Legislation Section
- Private Sector Banks Section
- Parliament Cell
- Reconstruction Section
- Returns Section
- Rajbhasha Anubhag
- Administration & Establishment Division
In the light of recent developments,
there has been increasing recognition of the need for strengthening of the
financial system to prevent its use for laundering proceeds of criminal
activities. To address and tackle the issues involved, AML Cell has been
recently set up in the Department. Its main activities are:
- Study of International Best Practices and Codes
on Anti - Money Laundering (AML) and Combating
Financing of Terrorism (CFT).
- Tracking domestic and global developments in AML
and CFT.
- Assessing India's position vis--vis international
regulatory and legal standards on AML/CFT formulated by Financial Action Task
Force (FATF), Bank for International Settlements (BIS), International Monetary
Fund (IMF) & Financial Stability Forum (FSF) on an ongoing basis.
- Correspondence with Government of India and its
agencies like Central Economic Intelligence Bureau and National Security
Council Secretariat, banks and other Departments of RBI on AML / CFT related
issues.
- Follow up of the decisions taken by the
Inter-Ministerial Co-ordination Forum for addressing issues relating to
financing of terrorism such as Financial Intelligence Unit, Suspicious
Transactions Reporting etc.
- Acting as Secretariat for 'Internal Co-ordination
Committee on Prevention of Money Laundering and Financing of Terrorism' of
RBI.
- Review of guidelines issued to banks on Know Your
Customer (KYC) and 'Cash Transactions'
- Preparation of briefs for top management for
meetings at domestic and international level with various organisations /
authorities.
- Taking up issues with AML implications such as
money transfer services with concerned authorities/organisations/RBI
departments.
- Study of the 'Prevention of Money Laundering Act'
and implications for Indian banks.
The key activity of the section,
appropriately named as Appointments Section, relates to the appointments of
authorities in the commercial banks, and also of members/directors on their
Boards, which may be elaborated as under:
- Approval of proposals from the domestic private
sector banks for appointment of part-time Chairman/Managing Director/
whole-time Chairman and Chief Executive Officers, as the case may be, as also
of the terms and conditions governing their appointments (Sections 10B &
35B of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949).
- Ensuring compliance with the provisions of the
Banking Regulation Act, 1949 with regard to the composition of the Board of
Directors of commercial banks in the private sector. (Sections 10A, 16 and 20
of the B.R. Act, 1949).
- Approval of proposals from foreign banks for
appointment of Chief Executive Officers (CEOs) in India (Section 35B of the
B.R. Act, 1949).
- Appointment of Chairman and Chief Executive
Officer in banking companies under Section 10BB of the B. R. Act, 1949, where
continuation of vacancy in the position is likely to adversely affect the
interest of the banking company.
- Appointment of observers in banking companies
under Section 36(1)(d)(iv) of the B. R. Act, 1949 where it becomes necessary.
- Removal of Chairman, Director, Chief Executive
Officer of banking companies under section 36AA of the B. R. Act, 1949, where
it becomes necessary.
- Making recommendations to Government regarding
constitution of the Central Board and Local Boards of State Bank of India
(Sections 19 and 21 of the State Bank of India Act, 1955).
- Approval of proposals for appointment of Managing
Directors and nomination of Directors, and also appointment of Additional
Directors and Alternate Additional Directors on the Boards of the subsidiary
banks of State Bank of India. [Section 25 of the State Bank of India
(Subsidiary Banks) Act, 1959]
- Making recommendations to Government regarding
appointment of Executive Directors/Chairmen & Managing Directors of public
sector banks, fixation of their salaries, payment of superannuation benefits
and other allied matters. [Clause 8 of the Nationalised Banks (Management and
Miscellaneous Provisions) Scheme 1970/1980].
- Making recommendations to Government regarding
appointment of non-official directors, non-workmen directors and RBI Nominee
Directors on the Boards of Nationalised banks. [Section 9 of the Banking
Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1970/1980].
- Monitoring of compliance with the provisions of
Section 10 of B.R.Act relating to appointment of CEOs in respect of private
sector banks under the jurisdiction of erstwhile MRO viz. Maharashtra and
Goa.
- Other items of work like clarifications on the
issues relating to the composition of banks Boards and their committees,
follow up work relating to implementation of the recommendations of the Report
of the Consultative Group of Directors of Banks/Financial Institiutions, etc.
The activities of the Branch Licensing
Section revolve around issue of authorisations to Indian commercial banks
including Local Area Banks for opening of branches in pursuance to regulatory
powers vested with Reserve Bank under the provisions of Banking Regulation Act,
1949. Over the period, this regime has been considerably liberalized,
deregulated and decentralized. The Section mainly undertakes the following
activities:
- To scrutinize applications from Indian Commercial
Banks for opening of branches, to issue letters of authorisations to the
concerned banks in this regard and advise the concerned ROs of the DBS to
issue necessary licences therefor.
- To consider requests received from banks for
shifting/closure of offices in semi urban/ rural areas, spinning off of
business and conversion of general/specialised branches, setting up of mobile
offices and satellite offices, and substitution of centres, and opening of
Extension Counters (ECs) / upgradation of ECs when it does not comply with
prescribed norms.
- To consider requests from ROs regarding extension
of validity period of licences/ /issue of fresh licences in lieu of the lapsed
ones.
- To consider representations/complaints from
institutions/VIPs and members of public for opening /shifting/closure of bank
offices.
- Review of branch licensing policy
periodically
- Maintenance and updation of database on
opening/substitution/closure/shifting of branches, Extension Counters, ATMs,
etc.
- Issue of licences to domestic banks for branches
etc. in Maharashtra and Goa and matters relating thereto.
- Issue of licences to foreign banks for branches
etc. in the country and matters relating thereto.
- Reconciliation of pending authorisations on half
yearly basis.
Banking Policy Section mainly attends
to the formulation of regulatory policy for commercial banks in India. It
undertakes various new policy initiatives and reviews existing guidelines for
progressive upgradation of prudential norms to move towards best practices. A
major element of financial sector reforms in India has been issue of a set of
prudential measures aimed at imparting strength to the banking system as well as
ensuring safety and soundness through greater transparency, accountability and
public credibility.
The major activities of the Section are
as follows:
- Formulation of policy and issue of prudential
guidelines pertaining to Capital adequacy; Income recognition; asset
classification and provisioning pertaining to advances portfolio;
Classification, valuation and operation of investment portfolio; and Credit
exposure limits
- Formulation of policy and issues regarding capital
structure of public sector banks, including raising of fresh equity, return of
capital, recapitalisation.
- Formulation of policy and issuance of regulatory guidelines for implementation of the Basel II framework.
- Policy guidelines / clarifications on integrated
risk management systems including Asset Liability Management and issue of
guidance notes on various aspects.
- Formulation of accounting policies pertaining to
areas not covered by the Accounting Standards issued by the Institute of
Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI).
- Rationalisation of existing disclosure norms and
prescription of additional disclosures to be made by banks in the "Notes on
Accounts" to their balance sheets for greater transparency and accountability.
- Clarifications on various accounting aspects and
those relating to banks balance sheets.
- Proposing policy initiatives for inclusion in the
Policy statements of Governor and co-ordinating work relating thereto.
- Formulation of proposals for inclusion in the
Union Budget and follow-up on budget announcements.
- Matters regarding delegation of powers to bank
functionaries, reservation for SC/ST in public sector banks (PSBs), tax
matters concerning banks, Calendar of reviews for public sector banks.
- Policy issues/ guidelines pertaining to compromise
settlement of NPAs of banks.
- Attending to court cases pertaining to all aspects
handled in the Section.
- Policy matters/ prudential guidelines pertaining
to reconciliation of inter-branch accounts, Nostro/Vostro/ Mirror accounts of
banks, clearing differences etc.
- Preparation of Consolidated Report on working of
Public Sector Banks for placing before the Parliament as per provisions of RBI
Act.
- Matters regarding Foreign Contributions
Regulations Act donations received by organizations from abroad.
- Contribution of material for inclusion in the
speeches of top management functionaries.
- Miscellaneous references on banking matters from
banks/public, Government and other departments of RBI.
- Preparation of discussion paper and providing
secretarial support to the Standing Technical Advisory Committee on Financial
Regulation.
- Preparation of agenda notes and follow up
pertaining to meetings of top management with Chief Executives of banks, Bank
Audit Committee Meetings.
- Compilation of material for meeting of Finance
Minister with Chief Executives of banks and follow-up action on action-points
emanating therefrom.
- Providing background papers and material for
discussions in meetings with officials of IMF / World Bank and other
international agencies,
providing information sought by such International
Agencies.
Moving with the winds of time and
international banking environment, the Departments function-base is steadily
and rapidly shifting to IT platform. Computer & Technology Cell has been set
up to attend to its computerisation requirements. Cells main activities
are:
- Policy matters pertaining to Internet Banking and
granting of approvals to banks request for offering Internet Banking Services
to their clientele.
- Providing inputs to the Department for references
relating to e-commerce, Internet banking and other technology related
issues.
- Approval on banks applications for membership of
INFINET.
- Maintenance of the Departmental LAN. Supervising
the maintenance of computer equipment, which is looked after by CMC and
others.
- Co-ordination with different user sections for
implementation of software applications development and monitoring the
application modifications as per request of users.
- Administration of Oracle database for CRR returns,
inward-outward dak application etc. including user creation, granting of
permissions to users in the Department and daily backups.
- Purchase of hardware such as PCs, Printers,
Laptops, Modems, Scanners, Servers and DLTs and software licenses like Win
2000, Bridge, Anti-Virus, Oracle, Domino
- Maintenance of Corporate and Internet e-mail
facility to officers, of Internet Accounts and Internet facilities, and of
Bridge station facility.
- Implementation of Banks IT Projects such as SFMS,
PKI, CDBMS etc. in the Department.
Reserve Bank of India is authorized to
issue directives to banks under Section 21 of Banking Regulation Act, 1949 in
the interest of depositors, members of public or banking policy. These
directives issued by the Directives Section mostly pertain to advances and
deposits of banks. However, there has been progressive deregulation over the
past decade.
The main activities of the Directives
Section relate to policy issues/guidelines/directives on
- Payment of Interest rates on various types of
deposit accounts (including NRI deposit), maintenance of deposit accounts,
prohibitions in respect of S.B. Accounts, matters relating to payment of
additional interest and brokerage on deposits, appointment of agents for
soliciting deposits, giving gifts/incentives to depositors/staff members,
freezing of accounts, Resurgent India Bonds, Development Bonds, etc.
- Interest rates on various categories of advances,
charging interest at quarterly or longer rests, rebate in interest rate, penal
interest, matters relating to Benchmark Prime Lending Rate stipulations,
modifications in loan documents, aggregation of limits, spread etc.
- Capital Market Exposure of banks - advances
against the security of shares, debentures, bonds etc., investments in shares,
debentures, mutual fund schemes, etc., matters relating to rediscounting of
bills, dematerialization of securities held as collateral, bridge loans,
etc.
- Matters relating to service Charges levied by the
banks, donation by banks and selective credit controls.
- Providing secretarial support to RBI-SEBI Standing
Technical Committee, which looks into areas of overlapping interest with
special emphasis on capital market regulation and endeavors for greater
regulatory harmonization.
The Cell was constituted to administer
the defaulters list schemes of the RBI, pursuant to the announcement by the then
Honble Finance Minister in his budget speech on February 28, 1994 that Reserve
Bank of India would be putting in place arrangements for circulating among banks
and financial institutions names of defaulting borrowers above threshold limit.
Its main items of work are:
- Collection and dissemination of information
from/to banks and notified All-India financial institutions (FIs) regarding
defaulting borrowers with outstanding aggregating Rs.1 crore and above, which
have been classified by them as 'doubtful' or 'loss' (non-suit filed accounts)
on half-yearly basis viz., as on March 31 and September 30.
- Collection and dissemination of information
from/to banks/FIs on cases of wilful defaults (non-suit filed accounts) with
outstanding aggregating Rs.25 lakh and above on quarterly basis.
- Policy matters and issues relating to wilful
defaulters and defaulter lists.
- Matters relating to Credit Information Bureau
(India) Ltd. (CIBIL) and rendering necessary assistance / guidance to CIBIL in
the matter of collection /
dissemination of credit information from / to banks / FIs.
- Other items of work like
complaints/representations from borrowers, directors of borrowing entities,
etc. about inclusion of their names in the Defaulter Lists, etc.
2. RBI was also disseminating said
defaulter lists of suit-filed accounts till the year 2002. However, the work
relating to collection and dissemination of credit information for said
defaulter lists of suit filed accounts as on March 31, 2003 and onwards has been
transferred to Credit Information Bureau (India) Ltd. Hence, RBI no longer deals
with defaulter lists of suit-filed accounts.
Gradual deregulation of the banking
system coupled with liberalisation of policies of Government and Reserve Bank of
India over the period, has led to a spurt in non-traditional banking activities
i.e. para - banking activities / financial services by the banks in exploration
of new and profitable business avenues through their extended arms
(subsidiaries) or departmentally. The major activities of the Cell are narrated
as under:
- The principal activity of the Cell continues to be
formulation of policy guidelines in respect of the diversified activities
undertaken by commercial banks departmentally or through subsidiaries such as
Asset-Management/Mutual Funds, Money Market Mutual Funds, Merchant Banking,
Factoring, Venture Capital, Credit / Debit /Smart card business, equity
participation in Venture Funds/ Leasing/Financial Companies, Housing Finance
and Primary Dealers.
- Examining applications from banks to set up
subsidiaries to undertake above-mentioned para-banking activities.
- Operational matters relating to banks' investments
in Govt. Securities.
- Examining applications from banks to introduce
off-line debit cards, variants of pre-paid cards, co-branded
debit/smart/pre-paid cards in tie-up with non-bank entities, etc.
- Formulation of policy on entry of banks into
insurance and processing of applications received from banks for entry into
insurance business either by way of subsidiary or Joint Venture (JV) on risk
participation basis or for strategic investment for agency business/referral
arrangements on fee basis and for setting up of insurance broking
subsidiaries.
- Follow-up with banks on closure/merger of
loss-making subsidiaries.
- Matters relating to introduction of rupee
derivatives/currency futures and options.
- Processing of proposals of banks to act as
settlement banks for Shared ATM Network, sharing of ATMs among banks,
etc.
- Processing of proposals of banks to become
professional clearing members of Multi-Commodity Exchange (MCX), National
Commodity & Derivative Exchange (NCDEX), equity participation of banks in
Multi-Commodity Exchange (MCX), National Commodity & Derivative Exchange
(NCDEX) and Asset Reconstruction Companies, etc.
- Matters relating to rediscounting of bills by SEBI
registered Mutual Funds, banks investment in Venture Capital Funds,
Investment Advisory Services (IAS), etc.
The globalisation of the economy in
early 1990s, open door policy of the Government coupled with liberal policy of
RBI, gave a tremendous boost to foreign banks presence in the country and of
Indian banks abroad. The activities of International Banking Section revolve
around these areas and could broadly be described as under:
I. Foreign banks operations in
India.
- Policy formulation regarding entry and expansion
of branches of foreign banks in India, opening of representative offices by
them in the country and their agency arrangements with Indian
firms/companies/individual etc. and examination of requests / proposal in this
respect and grant of approval / licenses therefor.
- Examination of cases of foreign banks investments
in immovable property in India.
- Monitoring of compliance by the foreign banks in
respect of Section 11 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, with capital
adequacy norms, single / group borrower-limits and dealing with requests for
relaxation in norms and scrutiny of their NPA returns.
- Review of entitlement of foreign banks for
engagement of expatriate staff and examination of their applications for
engaging expatriates over and above the entitlements.
- Dealing with references regarding shifting of bank
premises by foreign bank branches, cases of mergers /closures of their offices
and issue of necessary notifications.
- Processing of applications for data processing
abroad as well as in India in respect of Indian operations by foreign banks
operating in India and that of foreign bank branches in India.
- Examination of regulatory issues emanating from
Inspection Reports of foreign banks, received from Department of Banking
Supervision and follow-up thereof.
- Preparation of agenda papers for meetings of
Inter-Departmental Committee (IDC) of Government of India in respect of entry
of foreign banks in India, preparation of material for review notes on
presence and working of
foreign banks in India for submission to Central Board of Directors and
preparation of briefs on foreign banks for Governor / Deputy Governor /
Executive Director, etc., in connection with the meetings with officials of
foreign banks.
- Scrutiny and approval of applications made by
Authorised Dealers regarding posting of the Head of Treasury / Dealer / Chief
Dealer.
- Approval of consultancy agreement and
correspondent banking by foreign banks without having any presence in India
with Indian entities.
- Attending to references/cases received from
foreign banks for approval for exceeding single borrower / group borrower
exposure norms, merger/amalgamation/acquisition of foreign banks in India and
abroad, etc.
- Scrutiny of applications and furnishing of
comments to SEBI relating to registration of Foreign Institutional Investors
which are subsidiaries or associates of banks, with SEBI in India.
II. Indian banks operations
abroad
- Policy formulation and issue of guidelines
regarding overseas operations of Indian banks, examination of proposals and
grant of approvals for opening their Joint Ventures / Representative Offices /
branches and review of their overseas operations including closure of branches
/ joint ventures / representative offices.
- Approval of Indian banks proposals for entering
into Management Agreements and correspondent banking arrangements with foreign
entities.
- Preparation of proposals for submission before IDC
of GOI regarding opening of branches / representatives offices of Indian banks
abroad.
- Attending to cases received from Indian banks'
branches abroad for approval for exceeding single / group borrower
limits.
- Processing of requests from Indian banks for
remittance to comply with host country regulations in regard to their branches
abroad and
- handling of matters relating to compliance with
various prudential requirements of foreign branches of Indian banks.
- Applications for retention/transfer of profits
abroad/India by Indian banks.
- Processing of monthly/quarterly reports received
from Indian banks regarding their overseas branches.
- Co-ordination with DBS regarding operations of
Indian banks abroad.
III. Authorisation for dealing in
precious metals
Policy matters relating to Gold Deposit
and Gold Import Schemes and dealing with references received from banks in this
regard, issue and renewal of authorization for banks for import of gold / silver
/ platinum and acceptance of gold under Gold Deposit Scheme and collection of
data relating to import of gold and Gold Deposit Scheme and collection of data
relating to import of gold and gold deposits by banks in India.
IV. Offshore Banking
Units
- Approvals for setting up of Offshore Banking Units
(OBUs) and issue of policy guidelines for the operation of OBUs in Special
Economic Zones (SEZs).
- Correspondence with Government and other agencies
relating to setting up of Special Economic Zones, International Financial
Services Centres.
V. Other activities
- Attending to references from GOI and others for
banking / financial information / data etc. regarding Joint Commission
Meetings, visit of PM / FM to foreign countries.
- Matters relating to Indias Financial Services
under the General Agreement on Trade in Services in World Trade Organization
(WTO).
- Attending to references received from overseas
regulators viz. Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Monetary Authority of Singapore,
Financial Services Authority U K, and Federal Reserve Board USA in connection
with appointments of officers of Indian banks abroad.
- Residual items of work relating to Financial
Sector Development Project like co-ordination with the participating banks,
IDBI, DEIOand DAD on half-yearly repayment of
instalments and assisting World Bank Team in finalizing Project Completion
Report; and
- Approval of banks for soliciting deposits under
the Liberalised Remittance Scheme of USD 25000/- for resident
individuals.
As the name suggests, Information
Section serves as a nodal point for inflow and outflow of information and
interaction with other Departments of the bank and others in many areas. Its
important activities are:
- Compilation and supply of material for -
- Banks various publications like Annual Report,
Report on Trend and Progress of Banking in India, Report on Currency and
Finance and other reports like of Ministry of Finance, GOI, International
Monetary Fund, World Bank etc.
- Annual Report on activities of the Department
for Central Board of Directors and half-yearly and yearly report for Board
for Financial Supervision.
- Meetings of Central Board of Directors, Local
Boards, Governors/ DGs visits to states.
- Compilation of Monthly Report on the major
activities of the Department.
- Revision / amendments of the Manual of
instructions of the Department.
- Follow-up and compliance of the
observations/directions emanating from the meetings of BFS, Central Board of
Directors, Local Boards, Regional Directors letters to Governor, etc.
- Correspondence relating to Clearing House matters
like membership etc.
- Management of Library and related
activities.
- Supply of newspapers to Sections and Senior
Officers of the Department.
- Other matters like sale of Departments
publications, issue of quarterly list of circulars to banks.
The Industrial and Export Credit
Section (IECS) focuses on credit delivery issues concerning industrial, export,
infrastructure, housing and NBFC Sectors. The industrial credit segment has been
considerably liberalized / deregulated over the period. At present, various
items of work currently undertaken by IECS are distributed amongst three desks
viz. (i) Policy Desk (ii) Export Credit Desk and (iii) Industrial Rehabilitation
Desk, as under:
(i) Policy Desk
- Issues relating to industrial credit including
inter-institutional guarantees
- Issues relating to bank finance for infrastructure
projects
- Matters relating to financing of activities of
NBFCs by banks
- Macro-level policies for ensuring orderly growth
of housing finance extended by banks
(ii) Export Credit Desk
- Administration of the Export Credit Schemes (Pre
and Post-shipment credit in Rupees and Foreign currency), issue of
instructions to banks regarding the operation of Export Credit Scheme, and
prescribing ceiling interest rates on export credit as per the current
policies of the Bank and proposing policy changes viz. deregulation of
interest rates.
- Reviewing the policies and schemes to suit the
current needs of the exporters and as per the statements made in the Banks
Policy Statements / Exim Policy of the GOI, Ministry of Commerce (MOC).
- Attending to the suggestions received from the MOC
(GOI) and representations from exporters / Export Organisations / Trade Bodies
regarding changes in policy / procedures for extending export credit.
- Taking up matters connected with export credit
with other institutions such as ECGC, EXIM Bank, IBA, FEDAI, and banks.
- Convening of half yearly meetings of the All India
Export Advisory Committee as per the recommendation of the Estimates Committee
of Lok Sabha, for getting direct feed back from exporters, Export
- Organisations and banks regarding export credit
and Foreign Exchange related matters.
- Conducting quarterly seminars in centers of export
concentration for dissemination of information and to provide exposure to bank
officials to the policies and procedures connected with export credit and
export related foreign exchange matters.
- Formulation and implementation of new schemes for
the benefit for exporters viz. (i) Social financial package for large value
exporters and (ii) Gold Card Scheme for Exporters.
- Addressing current issues concerning exporters
viz. Availability of Packing Credit in Foreign Currency, Achievement of
Export Credit target by banks.
- Attending to complaints received from exporters
against banks with regard to timely provision of adequate export
credit.
- Conducting survey on level of satisfaction of
exporters with service rendered by banks and simplification of procedure for
delivery of bank credit and taking following action.
- Attending to WTO issues with reference to
anti-dumping / countervailing duty investigation by importing countries and
furnishing information and attending investigation meetings.
(iii) Industrial Rehabilitation
Desk
- Policy matters relating to rehabilitation of sick
and weak non-SSI industrial units including laying down broad parameters for
grant of reliefs and concessions.
- Correspondence with associations / federations
representing various industries including plantation/agro-based industries
such as coffee, tea, jute, sugar, tobacco, marine products etc.
- Monitoring of progress in implementation of
rehabilitation packages specifically approved by Reserve Bank of India.
Pursuant to the constitution of a Joint
Parliamentary Committee (JPC) to probe into the Stock Market Scam and matters
relating thereto by the Parliament in April 2001 and taking into account its
terms of reference, a coordination cell viz. JPC Cell was set up to ensure
overall coordination with various departments of the RBI and serve as a nodal
point for mainly attending to:
- Collection of information from the respective
departments and consolidation thereof, topic-wise/question-wise for
JPC.
- Preparation of appropriate replies to various
questions raised by members of JPC.
- References to GOI for necessary guidance/approval
on matters / issues relating to it.
2. JPC submitted its report to
Parliament on December 19, 2002. It has made in all 275
observations/recommendations, about one-third of which pertain to RBI. As a
follow-up measure, JPC Cell presently obtains comments/compliance on these
paras/recommendations of the report from respective departments in the Bank,
co-relates them and periodically submits compliance - progress reports to GOI as
a co-ordinator and interacts with GOI on the matters relating thereto.
Legislation Section, as the name
suggests, deals with various legislative matters relating to departmental work
areas. Its main activities can be enumerated as under:
- Interpretation of the various provisions of the
Banking Regulation Act, 1949, Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, etc.
- Examining and framing of rules/regulations and
amendments thereto in terms of State Bank of India Act, 1955 and SBI
(Subsidiaries) Act, 1959 and dealing with references relating thereto.
- Dealing with applications received from banks for
exemptions from the various provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949,
and Rules framed thereunder.
- Matters relating to contravention of the
provisions of sections 5,7,8,9,12,19,20 and 49A of the Banking Regulation Act,
1949, and Rules framed thereunder.
- The matters connected with the settlement of dues
through Lok Adalats and maintenance of database in respect of the feedback
received from banks.
- References / Work relating to declaration of
holidays under Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, of Non-Public Business
Working Day
- Periodical review of functioning of Debt Recovery
Tribunals and related matters and also maintenance of data base on quarterly
basis.
- Matters relating to Administration of Section 19
of the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act,
1970/80 covering Regulations relating to Officer Employees' service,
discipline and acceptance of jobs in private sector concerns after retirement,
bank employees' pension and Banks' General Regulations dealing with shares,
meetings of shareholders, election of directors, etc.
framing of new regulations, amendments to existing regulations, attending to
petitions filed by banks and private parties
challenging/invoking the various provisions of these regulation etc.
- Matters relating to customer service, viz.
Implementation of Goiporia Committee Recommendations and Citizens Charter
related matters thereto, Review of performance of Customer Service Centres and
their extension to other centers, speedy grievance redressal system, dealing
with references/complaints regarding customer service/certain complaints
arising out of banking practices
- Follow-up on the recommendations of the Committee
on Procedures and Performance Audit on public services in banks (Tarapore
Committee)
As the name reflects, Private Sector
Banks Section deals with various matters relating to domestic commercial banks
in the private sector - their setting up, their functioning and operations and
winding up as well as to Local Area Banks. Its major activities have been listed
below:
- Approval for transfer of shares and investments in
private sector banks.
- Approval for issue of shares viz. bonus shares,
preferential shares and also for public issues by private sector banks.
- Approval for declaration of dividend by private
sector banks.
- Appointment of non-official directors / nominee
directors on the boards of private sector banks.
- Sanction for recruitment of additional staff in
private sector banks where the banks are under direction.
- Granting of approval to private sector banks for
exceeding the prudential exposure limits prescribed.
- Approval for setting up new banks in the private
sector.
- Due diligence exercise on equity investors in
private sector banks.
- All matters pertaining to Foreign Direct
Investment on Automatic Route, Investment by FIIs etc. in private sector
banks.
- Approval for amalgamation of private sector
banks.
- Approval for amalgamation of an NBFC with a
private sector bank.
- Dealing with issues connected with take over bids
on banks
- Initiating action against directors / Chairmen of
banks and their removal, etc.
- Administering the provisions of Sections 7, 36AB,
44A and 45 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Issues relating to augmentation of capital by old
private sector banks.
- Vetting of proposals received from private sector
banks for opening of currency chests.
- Handling matters relating to dilution of
promoters' holding in the private sector banks.
- Miscellaneous references on banking matters from
private sector banks public / Government and other department's of RBI.
- Matters regarding reservation for SC / ST in
private sector bank, calendar of reviews for private sector banks.
- Matters relating to prior concurrence for
appointment / posting of forex dealers, Treasury Heads, etc.
- Attending to all other policy matters in respect
of private sector banks.
- Attending to all relevant matters relating to
Local Area Banks.
The Parliament Cell, as the name
suggests, deals with questions raised in Parliament by Honourable Members of
Parliament on banking matters and also redressal of grievances on the
department-related matters. Its activities may be enumerated as under:
-
- Dealing with Parliament Questions Coordination
within and outside the department for replies, processing and consolidation of
material and replies and their transmission to GOI and confirmation of such
replies given by GOI to Parliament Questions.
- Attending to Government references, Assurance
Questions, Oral evidence (replies), observations / Questionnaire etc of.
Estimate Committee / Standing Committee / Finance Committee etc.
- Dealing with
complaints/representations/suggestions received / published in the Newspapers
concerned with the functioning of the Department and sending a Monthly status
Report thereon to Department of Government and Bank Accounts.
Financially and operationally weak
banks are either reconstructed or amalgamated with other banking institutions in
the interest of depositors and the banking system of the country as a whole. The
banks are liquidated when reconstruction or amalgamation is not feasible.
Reconstruction Section deals with the matters in these areas as detailed below:
- Schemes of Amalgamations of banks under Section 45
of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949,
- Scheme of voluntary amalgamation of banks under
Section 44 A of the Act ibid.
- Scrutiny of yearly statements received from DBSs
Regional Offices in respect of the progress made in the implementation of the
schemes of amalgamations.
- References received from transferee banks for
writing-off of debts or assets taken to the collection accounts of transferor
banks, for debiting collection accounts of transferor banks with expenses not
provided for in the scheme etc.
- Post-merger problems e.g. representations by
employees of amalgamated banks regarding fixation of salary / grade and other
service conditions.
- Scrutiny of Final Valuation Statement of the
Assets and Liabilities of transferor banks and grant of approval for the
same.
- Scheme of arrangements of banks and others under
Section 44B of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Winding up petitions to courts under Section 38 of
the Act ibid in respect of banks granted moratorium under Section 45, which
cannot be reconstructed or amalgamated.
- Monitoring the progress in liquidation proceedings
of banks placed in liquidation; examination of statements received from
Regional Offices showing progress in liquidation proceedings and annual review
statements, matters relating to misfeasance proceedings involving directors /
officers of erstwhile transferor banks, etc.
Returns Section deals with the returns
of the banks relating to maintenance of cash reserve and statutory liquidity
ratios as required under Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and Banking Regulation
Act, 1949 and other statements / returns. Its items of work may mainly be
described as under:
- Monitoring and scrutiny of Form A returns and
monthly Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) statements from DBS Regional
Offices (ROs) and follow-up with them/banks in case of discrepancies
- Payment of interest to Scheduled Commercial Banks
(SCBs) on monthly basis on excess of Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) maintained above
the minimum statutory level of 3% of NDTL and upto the required level of CRR.
Receipt of penalties from banks due to shortfalls in maintenance of required
level of CRR.
- Monitoring receipt of Annexure I and III to Form
VIII returns from ROs for maintenance of Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and
follow up with ROs of DBS.
- Monitoring compliance with the provisions of
Section 11(2)(b) of Banking Regulation Act relating to statutory liquidity
requirement in respect of foreign banks in Maharashtra and Goa.
- Monitoring compliance with submission of various
other statutory returns by banks in Maharashtra and Goa.
- Charging of penal interest in cases of default in
SLR in respect of banks in Maharashtra and Goa and follow-up with banks and
Regional Offices of DBS for recovery of penal interest in case of default on
maintenance of SLR.
- Reporting to Monetary Policy Department (MPD) of
cases of waiver of penal interest.
- Attending to references received from DBS
regarding position of defaults in maintenance of CRR / SLR of banks.
- Monitoring submission of various statutory returns
to monitor compliance with CRR / SLR requirements by banks Preparation of
fortnightly / monthly abstracts Compilation of information relating to Press Communiqu in respect of banks in
Maharashtra and Goa and receipt of Press Communiqu data (including Annexure
A, B and C) from the ROs of DBS and its consolidation for transmission to MPD
/ Department of Economic Analysis and Policy (DEAP) and other user departments
on fortnightly basis.
- Monitoring statements from banks on Saving Bank
Accounts for time and demand liabilities portions thereof.
- Monitoring and scrutiny of Statements on Average
Daily Balances of Scheduled Commercial Banks with RBI received from Department
of Statistical Analysis and Computer Services (DESACS).
- Issue of instructions and attending to
correspondence with MPD/banks on various issues relating to policy
matters/clarifications on NDTL, eligibility of securities, maintenance of
CRR/SLR etc.
- Monitoring receipt of Form IX returns from ROs and
scrutiny thereof and Consolidation of Form IX in respect of all banks and
submission of the consolidated data to Government.
- Issuing instructions and attending to
correspondence regarding Telegraphic Transfers (TT), discounting facilities
and Remittance facilities.
- Monitoring receipt of Balance Sheets of Scheduled
Commercial Banks as required under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Advising clearing houses / Department of
Information Technology (DIT) regarding fixing limit of cheque presentation by
banks based on their deposit liabilities data.
The Section attends to the matters
pertaining to propagation of Rajbhasha Hindi in the Department as well as in the
public sector banks. It has the responsibility to implement official language
policy of Government of India (GoI) as required under the Official Language Act,
1963 and the Official Language Rules, 1976 and comply with the instructions
issued in this regard by the GoI from time to time. Thus, the activities of the
Section revolve around to fulfil the statutory obligations towards Rajbhasha and
can be stated as under:
(A) Use of Hindi in the
Department
- Translation of letters, circulars, notices,
notifications, publications and reports prepared in the Dept.
- Collecting quarterly progress reports on use of
Rajbhasha from various Sections / Cells of the dept. and consolidation,
analysis and review thereof for submission to Central Office
- Submitting monthly Demi-Official (D.O.) letters on
the progress of Hindi (in the Department) to Central Office (Rajbhasha
Department).
- Holding quarterly review meetings on the use and
progress of Hindi in the Dept.
- Collection and consolidation of information from
various sections regarding the visit, assurance etc. given by RBI to the
Committee of Parliament on Official Language, for submission to GOI.
- Taking follow up action on the decisions of the
Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC) of Central Office of the
Bank.
- Arranging Hindi training to help the staff to do
their work in Hindi including on computers.
- Advising on purchase of Hindi books and magazines
for Departments Library and organising Hindi Divas programmes in the
Department.
- Maintaining roster of eligible employees who are
required to undergo training under compulsory Hindi Teaching Scheme of GoI and
pass three exams., viz. Prabodh, Praveen and Pragya.
(B) Use of Hindi in public sector
banks
- Collection and consolidation of information from
various public sector banks regarding the visit, assurance etc. given by the
banks and/or RBI to the Committee of Parliament on Official Language.
- Arranging meetings of OLIC of banks,
consolidation, analysis and review of quarterly progress of public sector
banks, bank-wise and region-wise, for submission in the meetings and taking
follow-up action on their decisions.
- Periodically monitoring progress of work in Hindi
on computers in bank branches.
- Providing list of bank offices/branches, wherein
80% or more staff knows Hindi, to the GOI for publication in the Gazette of
India as required under Section 10(4) of Official Language Rules, 1976.
- Providing necessary guidance and assistance to
banks in implementation of OL Policy including preparation and publication
literature therefor like Computer Paribhasha Kosh.
- Arranging the annual Rajbhasha Sammelans of public
sector banks and financial institutions and taking appropriate action on the
proposals of the Sammelans.
- Organising or assisting the public sector bank(s)
to organize the seminars / lectures /demonstrations / presentations etc.
relating to IT and Rajbhasha.
- Collecting and providing the information to the
GOI on Parliament questions, providing necessary help and also taking the
follow up action on the decisions of OLIC of Banking Division, GoI, and
attending to the work pertaining to the Town OLICs.
Administration and Establishment
Division deals with administration and establishment matters relating to the
Department which are dealt through following major Sections / Cells:
- Staff Section (I, II, III)
- Planning & Budget Cell
- Leave Section
- Accounts Section
- Provident Fund / Gratuity / Pension Cell
- Housing Loan Section
- Medical Section
- Salary Section
- General Section
- Records Management Cell
The functions of the above sections /
cells are reflected in their names themselves and hence need no description.
However, as DBOD is a separate accounting unit, Accounts Section accounts for
the vouchers emanating from various types of bills and other payments in the
Department. It also acts as the nodal point for all inter-office transactions
emanating in RBI General A/c and Central Office Transactions A/c. Planning &
Budget Cell, besides preparing the budget of the department, also does the
co-ordination work relating to compliance of Inspection / Audit Reports of the
Department. General Section attends to general administrative requirements
including maintenance of premises.
Besides, the Division attends to
certain administrative and establishment functions of Department of Banking
Supervision and Department of Non-Banking Supervision and also looks after Staff
- Dispensary and Officers Lounge and Dining Room.
A few more words.
This handbook is intended to broadly
familiarize the readers with the functions and working of the Department, which
has been instrumental in putting the banking sector on reforms path backed with
the 'open-door policy' of the Government, particularly since 1990. The
Department has a flexible set up and dynamic approach to meet the emerging
global challenges, changing banking environment and demands of the rapidly
growing economy. This necessitates an on-going process of readjustment of
operational areas amongst functional groups, streamlining of systems and
procedures and review of work-process. Hence, 'changes to meet challenges' is
our motto as DBODians proudly say.
|