The annual survey on ‘International Trade in Banking Services’ (ITBS) provides information on financial services rendered by overseas branches/subsidiaries of Indian banks and branches/subsidiaries of foreign banks operating in India, based on explicit/implicit fee/commission charged to customers. The results of the 2014-15 round of ITBS survey are presented here. It covers the broad changes in branch/ employee/country profile of their banking business as well as service activities (both fund and non-fund based). The major trend in their balance sheet, income, expenditure and profitability are also discussed. Introduction International trade in banking services cover banking services provided to residents of an economy through local presence of (a) foreign banks and (b) foreign affiliates. It takes into account services such as deposit-taking, lending to firms, mortgage lending, consumer finance, and a host of so-called non-asset-based services such as securities underwriting, local currency bond trading, foreign exchange trading, brokering, custody services, funds transfer and management services and financial consultancy/ advisory services. The globalisation of Indian economy has witnessed cross-border direct investments in banking in the form of branches, agencies and subsidiaries, or by the means of cross-border mergers and acquisitions. Over the years, the number of banks branches/subsidiaries have increased for both Indian and foreign banks to provide cross-border banking services. It is useful to assess the efficiency of such banking services by Indian banks operating abroad and foreign banks operating in India. Also, the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) under the World Trade Organisation (WTO) inter alia, necessitated the need of consistent and comparable statistics on ITBS for assessing the financial services sector liberalisation. The ITBS survey, conducted annually by the Reserve Bank since 2006-07, is intended to provide information on financial services provided locally through commercial presence [i.e., Mode-3 of supply as per the Manual of Statistics of International Trade in Services (MSITS)] for the banking sector. These cover overseas branches/subsidiaries of Indian banks operating abroad and foreign banks operating in India. As per IMF’s Balance of Payments and International Investment Position Manual: Sixth edition (BPM6), subsidiary is a direct investment enterprise (DIE) over which direct investor is able to exercise control, which is assumed to exist if the investor has more than 50 per cent share in total equity of the enterprise. The 2014-15 survey round covered 178 overseas branches and 235 overseas subsidiaries of Indian Banks and 313 branches of foreign banks operating in India. The salient features along with the trends in the international trade in banking services in the last few years are analysed here1. As all scheduled commercial banks with cross-border presence responded to the survey, the results present census position though the data for the latest year remain provisional. I. Branch Distribution Cross-border presence of Indian banks has increased over the years in line with the growing demands from cross-border trade and other activities. The number of overseas branches of Indian banks stood at 178 as on March 2015 (from 153 four years ago), of which, the highest number of branches were located in the United Kingdom (31), followed by Hong Kong (19), Singapore (17), United Arab Emirates (13) and Sri Lanka (13). Public sector banks dominated the overseas presence of Indian banks, where State Bank of India had the largest overseas presence (55 branches in 21 countries) followed by Bank of Baroda (47 branches in 14 countries). The number of branches of foreign banks in India increased marginally in 2014-15, after a decline in 2013- 14. The trend of contraction in the employee strength of foreign banks operating in India witnessed since 2011-12, has reversed during 2014-15 when the workforce increased by 3.3 per cent. The total number of employees of Indian banks’ branches operating abroad was marginally lower than the previous year’s level. Indian banks’ branches operating abroad employed 62.5 per cent of employees from local sources, 33.9 per cent from India and remaining 3.6 per cent from other countries. On the other hand, 99.4 per cent of foreign banks employees working in India were local (Chart 1). II. Banking Business The business of both Indian banks’ overseas branches as well as foreign banks operating in India continued to grow albeit at a slower pace than witnessed in the previous year. In 2014-15, their consolidated balance sheet increased by 13.5 per cent and 2.8 per cent, respectively, as compared with 28.7 per cent and 20.3 per cent, witnessed in 2013-14. The consolidated balance sheet of overseas subsidiaries of Indian banks also grew at a slower pace of 1.8 per cent in 2014-15 (23.9 per cent in 2013-14). However, since March 2010, the combined balance sheet of overseas branches of Indian banks recorded more than 160 per cent increase in US dollar terms whereas the combined balance sheet of foreign banks in India increased by around 25 per cent. | Table 1: No. of Branches and Employees – 2010-11 to 2014-15 | | Category | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | | No. of Branches | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | 153 | 163 | 170 | 170 | 178 | | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | 150 | 158 | 184 | 235 | 235 | | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | 309 | 309 | 316 | 307 | 313 | | | No. of Employees | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | 3,289 | 3,489 | 3,761 | 3,915 | 3,897 | | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | 2,325 | 2,580 | 2,818 | 3,469 | 3,424 | | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | 28,158 | 27,342 | 25,118 | 24,703 | 25,519 | The share of credit in total assets of overseas branches of Indian banks stood at 57.4 per cent in March 2015, which is lower than the corresponding share of overseas subsidiaries of Indian banks (70.7 per cent), but higher than the share of the foreign banks operating in India (44.8 per cent). However, the share of deposits in total liabilities of Indian banks’ overseas branches (at 39.0 per cent) remained lower than the corresponding share of their subsidiaries (58.1 per cent) and the share of the foreign banks operating in India (53.7 per cent) as witnessed in the past (Table 3). | Table 2: Type of Employees – 2013-14 and 2014-15 | | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | Total number of branches | 170 | 178 | 235 | 235 | 307 | 313 | | Number of Employees | 3,915 | 3,897 | 3,469 | 3,424 | 24,703 | 25,519 | | of which: | | | | | | | | Local | 2,393 | 2,437 | 2,829 | 2,832 | | | | Indians | 1,210 | 1,322 | 548 | 469 | 24,561 | 25,354 | | Others | 312 | 138 | 92 | 123 | 142 | 165 |
| Table 3: Bank Balance Sheet – 2010-11 to 2014-15 (End-March) | | Category | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | | Credit to Total Assets (%) | 61.2 | 60.2 | 58.9 | 58.5 | 57.4 | | Deposits to Total Liabilities (%) | 37.2 | 36.5 | 39.5 | 39.0 | 39.0 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (₹ billion) | 5,720.5 | 7,399.2 | 9,939.8 | 12,791.2 | 14,520.0 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (US$ billion)* | 128.1 | 144.6 | 182.8 | 212.8 | 232.0 | | | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | | Credit to Total Assets (%) | 62.3 | 64.9 | 66.5 | 67.9 | 70.7 | | Deposits to Total Liabilities (%) | 69.5 | 59.5 | 55.2 | 58.2 | 58.1 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (₹ billion) | 736.5 | 826.4 | 848.3 | 1,050.9 | 1,069.5 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (US$ billion)* | 16.5 | 16.2 | 15.6 | 17.5 | 17.1 | | | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | | Credit to Total Assets (%) | 40.4 | 41.9 | 50.7 | 40.8 | 44.8 | | Deposits to Total Liabilities (%) | 49.0 | 46.9 | 46.7 | 47.8 | 53.7 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (₹ billion) | 4,904.8 | 5,764.5 | 6,066.5 | 7,290.3 | 7,497.6 | | Total Assets/Liabilities (US$ billion)* | 109.8 | 112.7 | 111.5 | 121.3 | 119.8 | Growth in credit extended and deposit mobilised by Indian banks’ overseas branches moderated to 11.3 per cent and 13.3 per cent respectively, during 2014-15 as compared with the growth of 27.9 per cent and 27.0 per cent, respectively in the previous year. In contrast, the credit extended by foreign banks operating in India increased by 13.0 per cent in 2014-15 against a decline of 3.4 percent in the previous year. The asset base of Indian banks’ overseas subsidiaries remained much lower as compared to their overseas branches. Credit and deposit of overseas subsidiaries of Indian banks increased moderately by 5.9 and 1.6 per cent, respectively, on top of high growth of 26.6 and 30.7 per cent, recorded in 2013-14. III. Income and Expenditure The total income of Indian banks’ overseas branches (IB_O_Br) and their subsidiaries (IB_O_Sub) operating abroad and foreign banks operating in India (F_Br_I), increased in 2014-15. Total income of Indian banks’ overseas branches grew by 8.1 per cent in 2014- 15 (9.4 per cent in 2013-14), whereas it increased for their overseas subsidiaries by 5.2 per cent in 2014-15 (16.9 per cent in 2013-14). Total income and expenditure of foreign banks operating in India grew by 10.3 and 9.6 per cent, respectively, in 2014-15 (11.1and 19.8 per cent in the previous year). Foreign banks in India had higher share of non-interest income when compared to overseas branches of Indian banks. During 2014-15, the share of non-interest income in total income was 13.9 per cent for overseas branches of Indian banks and 22.9 per cent for foreign banks operating in India (Chart 3, Table 4). 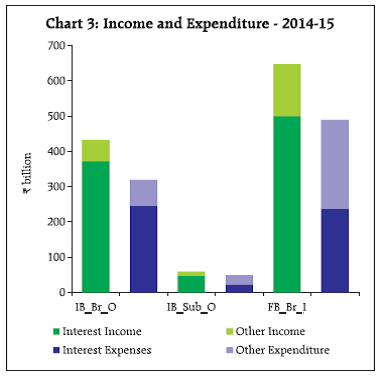
| Table 4: Income and Expenditure– 2010-11 to 2014-15 | | (Amount in ₹ billion) | | | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | | Income | 196.6 | 285.3 | 365.6 | 399.8 | 432.3 | | Expenditure | 134.0 | 206.2 | 273.7 | 306.4 | 318.8 | | | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | | Income | 38.1 | 42.1 | 48.0 | 56.1 | 59.0 | | Expenditure | 29.7 | 33.9 | 34.3 | 45.8 | 48.4 | | | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | | Income | 394.3 | 467.3 | 528.4 | 587.2 | 647.7 | | Expenditure | 281.3 | 327.9 | 372.6 | 446.5 | 489.5 | IV. Profitability Profitability of foreign banks in India remained substantially higher than the overseas branches/ subsidiaries of Indian banks. In 2014-15, the profitability ratio (profit-to-assets) as well as income-to-asset ratio showed some increase in case of foreign banks operating in India whereas for overseas branches/ subsidiaries of Indian banks, the ratios remained around the previous years’ level (Charts 4A & 4B). Country-wise return on asset (ROA) indicate that Indian bank branches operating in Maldives recorded the highest return on assets (3.4 per cent) followed by banks in Bangladesh (3.2 per cent) during 2014-15. In countries with larger number of branches, the ratio was lower at 0.8 per cent for Hong Kong, 0.4 per cent for UK and 0.3 per cent for Singapore (Chart 5). V. Activity-wise Trade in Banking Services Information on trade in banking services was collected based on explicit and implicit fees or commission charged to the customers for various banking services rendered. For this purpose, the financial services provided by them were classified into eleven major groups as per the MSITS, and detailed data were collected. During 2014-15, overseas branches of Indian banks generated more fee income by rendering banking services, mainly due to higher focus on ‘Credit related services’, ‘Derivative, stock, securities, foreign exchange trading services’ and ‘Trade finance related services’. On the other hand, the fee income generated by their overseas subsidiaries were mainly due to ‘Trade finance related services’, ‘Credit related services’ and ‘Payment and money transmission services’. Foreign banks operating in India received major part of their fee income from ‘Derivative, stock, securities, foreign exchange trading services’, ‘Payment and money transmission services’, ‘Financial consultancy and advisory services’ and ‘Trade finance related services’ (Table 5, 6). | Table 5: Activity-wise Composition of Banking Services delivered by Overseas Branches of Indian Banks and Subsidiaries of Indian Bank | | (Amount in ₹ billion) | | Banking Service | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | Indian Banks' Subsidiaries Operating Abroad | | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | Deposit Account Management Services | 0.9 | 1.8 | 7.8 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 4.1 | 0.2 | | Credit Related Services | 23.9 | 25.6 | 40.5 | 24.9 | 26.6 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 2.5 | | Financial Leasing Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Trade Finance Related Services | 10.6 | 18.2 | 34.4 | 14.3 | 15.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 5.0 | 5.2 | | Payment and Money Transmission Services | 2.6 | 10.1 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.2 | | Fund Management Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.0 | | Financial Consultancy and Advisory Services | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.8 | | Underwriting Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Clearing and Settlement Services | 0.0 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Derivative, Stock, Securities, Foreign Exchange trading Services | 4.5 | 9.6 | 3.1 | 19.8 | 19.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | | Other Financial Services | 0.5 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 25.2 | 26.8 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.5 | | Total | 44.0 | 68.0 | 93.5 | 89.6 | 94.3 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 16.6 | 13.0 | | Note: Sum of components may differ from total due to rounding off. This is applicable for other tables also. |
| Table 6: Activity Share in Trade in Banking Services | | (per cent) | | Activity | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | Deposit Account Management Services | 2.1 | 2.7 | 8.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 2.8 | | Credit Related Services | 54.4 | 37.6 | 43.2 | 27.8 | 28.2 | 9.0 | 10.9 | 12.2 | 11.9 | 12.0 | | Financial Leasing Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Trade Finance Related Services | 24.2 | 26.8 | 36.7 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 11.1 | 19.0 | 22.1 | 17.1 | 16.6 | | Payment and Money Transmission Services | 6.0 | 14.8 | 5.7 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 17.5 | 9.2 | 15.0 | 15.7 | 18.3 | | Fund Management Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 5.6 | | Financial Consultancy and Advisory Services | 2.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 14.1 | 14.4 | 15.0 | 16.6 | 17.2 | | Underwriting Services | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 0.6 | | Clearing and Settlement Services | 0.0 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 3.7 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.7 | | Derivative, Stock, Securities, Foreign Exchange trading Services | 10.2 | 14.1 | 3.5 | 22.1 | 20.8 | 27.1 | 21.5 | 17.6 | 20.9 | 20.4 | | Other Financial Services | 1.0 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 28.0 | 28.4 | 9.8 | 9.6 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 5.9 | | All activities | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | VI. Fee Income Total fee income generated by the 178 overseas branches of Indian banks increased to ₹94.3 billion (US$1.5 billion) in 2014-15 from ₹89.6 billion (US$ 1.5 billion) in the previous year, whereas fee income of 313 branches of foreign banks operating in India reduced to ₹72.7 billion (US$1.2 billion) in 2014-15 from ₹78.8 billion (US$ 1.3 billion) in 2013-14 (Chart 6). A dominant portion of fee income of Indian banks’ overseas branches came from residents. In contrast, major portion of fee income for Indian banks’ subsidiaries abroad that came from residents till previous year has changed in 2014-15 (Chart 7).
In terms of fee income, branches of Indian banks in UK had the largest contribution in providing banking services followed by UAE, Hong Kong and Singapore (Table 7). The amount accrued from ITBS operations of foreign banks from USA, Hong Kong and Japan in India was higher than the amount accrued from such overseas operations by Indian banks in these countries. | Table 7: Country-wise classification of Fee Income by Overseas branches of Indian Banks and Foreign Banks Operating in India | | (Amount in ₹ billion) | | | Indian Banks' Branches Operating Abroad | Foreign Banks’ Branches in India | | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | | Bahrain | 3.7 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | | Belgium | 0.8 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | | Hong Kong | 5.7 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 12.4 | 16.5 | 15.7 | 13.4 | 13.5 | | Japan | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.4 | | Singapore | 7.6 | 8.9 | 8.2 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 2.0 | 4.6 | 3.6 | 2.3 | 2.2 | | Sri Lanka | 0.2 | 0.1 | 15.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | | UAE | 5.2 | 5.9 | 4.1 | 8.5 | 9.9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | | UK | 10.5 | 27.8 | 38.8 | 49.8 | 52.3 | 25.5 | 26.8 | 18.5 | 23.0 | 18.5 | | USA | 4.4 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 34.2 | 24.0 | 20.4 | 26.6 | 25.6 | | Other Countries | 4.9 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 31.4 | 20.7 | 14.4 | 11.7 | 10.9 | | Total | 44.0 | 68.0 | 93.5 | 89.6 | 94.3 | 106.7 | 94.3 | 74.5 | 78.8 | 72.7 | VII. Conclusion The increase in the international presence of Indian banks and that of foreign banks in India over the years points towards the rising global demand for international trade in banking services. The consolidated balance sheet of overseas branches of Indian banks, which moderated after the global financial crisis, recovered in subsequent years. Since March 2010, the combined balance sheet of overseas branches of Indian banks has recorded much higher increase than the combined balance sheet of foreign banks in India. Despite lower asset base, the total income of foreign banks’ branches in India consistently exceeded the income of overseas branches of Indian banks during the last five years. Fee income has gained significant focus as a source of revenue in recent years and a dominant portion of the fee income of Indian banks’ branches operating abroad came through rendering services to residents. The share of non-interest income in total income of foreign banks in India was higher than that for overseas branches of Indian banks. Profitability ratio of foreign banks in India remained above that of the overseas branches/subsidiaries of Indian banks.
|