International Banking Statistics of India: September 2006*
The article presents international liabilities and assets of banks in India,
classified under Locational Banking Statistics (LBS) and consolidated international/foreign
claims under Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS), compiled as per the International
Banking Statistics system of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), for
the quarter ended September 2006. These data are compared with those as at the
end of the previous quarter and a year ago. The analysis of international liabilities/assets,
based on LBS, has been presented by instrument, country and sector of customer/borrower,
currency and country of incorporation of reporting bank; and the consolidated
international claims, based on CBS, according to country and sector of borrower
and residual maturity. Further, a broad comparison of international/foreign claims
of BIS reporting banks vis-à-vis Indian Banks as at the end of September
2005 and 2006 has also been covered. Besides, this article details international/
foreign claims derived from on-balance sheet items, viz., loans and deposits,
holdings of securities as well as off-balance sheet items, viz., derivatives,
guarantees and credit commitments on ultimate risk basis. * Prepared in
the Banking Statistics Division of the Department of Statistical Analysis and
Computer Services. The previous article on the subject as at end-June 2006 was
published in January 2007 issue of the Bulletin. I. Introduction
Eighty-five commercial and co-operative banks, which are authorised to deal in
foreign exchange and accept non-resident deposits (Indian Rupee and foreign currencies),
have furnished information under the International Banking Statistics (IBS) system,
as per the reporting system of the BIS. These banks submit the consolidated data
of their reporting branches/offices. The foreign branches of Indian Banks also
submit data on international claims, which are included in the consolidated position
of the Indian Banks’ international/foreign claims. The BIS reporting system
of IBS has been revised from the reporting quarter March 2005, which, inter
alia, covers the claims of domestic reporting banks arising from derivatives,
guarantees and credit commitments. Accordingly, international/foreign claims on
ultimate risk basis of domestic reporting banks for the quarter ended September
2006 have been compared with those of the previous quarter and a year ago in this
article. A comparative picture of the CBS of the BIS reporting countries and CBS
of India for the third quarter of 2006 with corresponding quarter of 2005 is also
presented in the article@ .
II. Data Coverage and Methodology@@ The
data cover authorized dealer (AD) branches of 85 reporting banks as at end-September
2006. Of these banks, 57 are Indian Banks (28 public sector banks including IDBI
Ltd., 26 private sector banks and 3 co-operative banks) and 28 are foreign banks.
The branches maintaining nonresident Rupee deposits like Non-Resident External
Rupee (NRE) deposits and NonResident Ordinary (NRO) Rupee deposits are also covered.
Further, banks’ branches report, inter alia, the detailed data
on international liabilities and assets in actual currency [24 major foreign currencies
and domestic currency (INR)] of transaction in IBS return. The international liabilities
of banks covered in IBS (as defined by the BIS) and external debt reported by
the banking sector in India are not strictly comparable, since certain items of
liabilities, like, American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), Global Depositary Receipts
(GDRs), equity of banks held by non-residents, included in IBS, are not part of
the external debt. @ A brief outline of the BIS reporting system of IBS
comprising LBS and CBS, purpose of IBS, BIS reporting area for IBS, the distinction/relation
between IBS of India vis-à-vis external debt of India has been provided
in the Article published in August 2006 issue of the RBI Bulletin.
@@ The methodology of compilation of LBS/CBS and explanation to various terms
used in IBS has been provided in the article on the subject published in August
2006 issue of the RBI Bulletin. III. The Results
III.1 Locational
Banking Statistics (LBS)
International Liabilities/Assets The
international liabilities as well as the international assets of banks increased
as at end-September 2006 over the previous quarter. However, the international
liabilities of banks were almost double than their international assets (Chart
1). The mismatch between the two for banks in India could be attributed to
deployment of the funds mobilized from abroad, in the domestic market in the domestic
currency. The international liabilities of banks increased by Rs. 14,236 crore
(4.4 per cent) and Rs. 46,127 crore (16.0 per cent) as at end-September 2006 over
the position in the previous quarter and a year ago, respectively (Table
1). While the increase over previous quarter was mainly due to considerable
increase in equities of banks held by non-residents and ADRs/GDRs, the increase
over the position a year ago was mainly due to rise in equities of banks held
by non-residents, ADRs/GDRs, foreign currency borrowings, FCNR(B) deposits and
NRE deposits. The liabilities denominated in foreign currencies accounted for
50.6 per cent of the total international liabilities as at end-September 2006
registering a substantial decline over the share of 57.5 per cent a year ago.
The decline in liabilities in foreign currencies was due to redemption of India
Millennium Deposits (IMDs) in December 2005 and sizeable increase in rupee denominated
equities of banks held by non-residents, thus, increasing the share of rupee liabilities
towards non-residents. 
Table 1: International
Liabilities and Assets of Banks in India | (Branches
of Indian and Foreign Banks in India) | Items | Amount
Outstanding # as on | | September
30, 2005 | June
30, 2006 | September
30, 2006 | | Rs. | US
$ | Rs. | US
$ | Rs. | US
$ | | crore+ | million | crore+ | million | crore+ | million |
International Liabilities | | | | | | |
Liabilities to Residents and Non-residents | 166,043 | 37,720 | 167,007 | 36,274 | 169,497 | 36,907 |
denominated in Foreign Currencies | (57.5) | (57.5) | (52.1) | (52.1) | (50.6) | (50.6) |
Liabilities to Non-residents | 122,828 | 27,903 | 153,755 | 33,396 | 165,501 | 36,037 |
denominated in Indian Rupees | (42.5) | (42.5) | (47.9) | (47.9) | (49.4) | (49.4) |
Total International Liabilities + | 288,871 | 65,623 | 320,762 | 69,670 | 334,998 | 72,945 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
International Assets | | | | | | |
Foreign Currency(FC) Assets (includes FC
Loans | 130,813 | 29,717 | 147,457 | 32,028 | 155,571 | 33,875 |
to Residents and Non-residents, Outstanding | (96.8) | (96.8) | (95.6) | (95.6) | (95.4) | (95.4) |
Export Bills, FC Lending to Banks in India, | | | | | | |
FC Deposits with Banks in India, Overseas | | | | | | |
FC Assets, Remittable Profits of Foreign | | | | | | |
Branches of Indian banks, etc.) | | | | | | |
Assets in Indian Rupees with Non-residents | 4,390 | 997 | 6,747 | 1,465 | 7,420 | 1,616 |
(includes Rupee Loans to Non-residents | (3.2) | (3.2) | (4.4) | (4.4) | (4.6) | (4.6) |
out of Non-resident Deposits) | | | | | | |
Total International Assets | 135,203 | 30,714 | 154,204 | 33,493 | 162,991 | 35,491 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
+ : 1 crore= 10 million. The
FEDAI revaluation rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at end-September 2005,
June 2006, and September 2006 were Rs. 44.020, Rs 46.040 and Rs. 45.925 per US
Dollar, respectively.
# : Data pertain to only reporting branches. As such,
these data provide broad dimensions of international assets
and liabilities,
Notes : 1. All figures are inclusive of accrued interest.
2. Figures in brackets
represent percentages to total international assets.
3. Sum of the components
may not tally with total due to rounding off .
4. Data have been revised for
previous quarters. | The international assets increased
by Rs. 8,787 crore (5.7 per cent) as at end-September 2006, over the position
in the previous quarter. Though there was a decline in foreign currencies loans
to residents, the growth was due to considerable increase in NOSTRO balances and/or
placements held/ made abroad. The international assets denominated in foreign
currencies accounted for 95.4 per cent of total international assets as at end-September
2006 as compared with 95.6 per cent in the previous quarter and 96.8 per cent
a year ago. International Liabilities Vs External Debt of Indian Banking
System
Details of international liabilities, in US dollar terms,
classified into items that are included under external debt statistics and those
not covered under external debt statistics, are presented in
Table 2. The external debt part of international liabilities of banks in India,
which covers FCNR(B) Deposits, NR(E)R Deposits, foreign currency borrowings, Bonds,
FII deposits, etc., declined by US $ 1 million over the position in the
previous quarter and stood at US $ 54,743 million as at end-September 2006. Even
after offsetting the impact of redemption of India Millennium Deposits (IMDs),
external debt increased by US $ 266 million over the position a year ago. India’s
external debt increased by US $ 4,313 million from US $ 132,203 million as at
end-June 2006 to US $ 136,516 million as at end-September 20061 . Non-debt liabilities
(American Depository Receipts, Global Depository Receipts, equities of banks held
by non-residents and capital of foreign banks’ branches in India) increased
by US $ 3,288 million in September 2006 over June 2006. Foreign currency liabilities
towards residents increased to US $ 2,665 million as at end-September 2006 as
compared with US $ 2,588 million in June 2006 and US $ 2,077 million a year ago.
Table 2: International Liabilities
of Banks in India | (US
$ million) | Categories
/ Items | Amount Outstanding
as at end | | | | | September | June | September |
| | | | 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
I. | | Items
included under External Debt Statistics + | 54,477 | 54,744 | 54,743 |
| | 1. | Foreign
Currency Non-Resident Bank [FCNR(B)] Schemes | 11,763 | 13,876 | 14,356 |
| | 2. | Non-Resident
External (NRE) Rupee A/Cs | 21,589 | 23,020 | 23,483 |
| | 3. | Foreign
Currency Borrowings (includes Inter-bank Borrowings and External | | | |
| | | Commercial
Borrowings of banks) other than through ADRs, GDRs, Bonds, etc. | 13,476 | 15,293 | 14,487 |
| | 4. | Bonds
(including India Millennium Deposits) | 6,881 | 1,000 | 997 |
| | 5. | Floating
Rate Notes (FRNs) | 1 | — | — |
| | 6. | Foreign
Institutional Investors’ (FII) A/Cs | 767 | 1,456 | 1,318 |
| | 7. | Other
Own issues of Intl. Debt Securities | — | 100 | 100 |
II. | | Items
not included under External Debt Statistics | 1,361 | 1,352 | 1,347 |
| | 1. | Embassy
A/Cs | 33 | 40 | 44 |
| | 2. | ESCROW
A/Cs | 12 | 6 | 3 |
| | 3. | Non-Resident
Ordinary(NRO) Rupee Deposits | 1,316 | 1,306 | 1,299 |
III. | Non-Debt
Liabilities (not included in External Debt due to definitional aspects) | 7,220 | 10,629 | 13,917 |
| | 1. | American
Depository Receipts(ADRs) and Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) | 2,979 | 2,844 | 3,836 |
| | 2. | Equities
of Banks held by NRIs | 2,007 | 5,040 | 7,264 |
| | 3. | Capital
of foreign banks/branches in India and Certain Other Items in Transition | 2,234 | 2,745 | 2,817 |
IV. | FC
Liabilities to Residents (not included in External Debt due to | | | |
| | definitional
aspects) + | 2,077 | 2,588 | 2,665 |
| | 1. | Exchange
Earners’ Foreign Currency (EEFC) A/Cs | 1,361 | 1,507 | 1,570 |
| | 2. | Resident
Foreign Currency (RFC) Deposits | 318 | 370 | 330 |
| | 3. | Inter-Bank
Foreign Currency Deposits and other Foreign | | | |
| | | Currency
Deposits of Residents | 397 | 712 | 765 |
V. | | Other
Items of International Liabilities (not included in External Debt | | | |
| | due
to definitional aspects) | 488 | 357 | 272 |
| | 1. | Balances
in VOSTRO A/Cs of Non-resident Banks and Exchange Houses | | | |
| | | (including
term deposits) | 488 | 357 | 272 |
VI. | Total
International Liabilities (I+II+III+IV+V) | 65,623 | 69,670 | 72,945 |
+ : Data as reported under IBS do not cover
all branches and are not comparable with data reported by all bank branches under
a different set of data.
Notes :
1. All figures are inclusive of accrued
interest.
2. The FEDAI revaluation rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at
end-September 2005, June 2006, and
September 2006 were Rs. 44.020, Rs 46.040
and Rs. 45.925 per US Dollar, respectively.
3. Data have been revised for
previous quarters. | International Liabilities
Vs External Debt of Indian Banking System
Details of international
liabilities, in US dollar terms, classified into items that are included under
external debt statistics and those not covered under external debt statistics,
are presented in Table 2. The external debt part of international liabilities
of banks in India, which covers FCNR(B) Deposits, NR(E)R Deposits, foreign currency
borrowings, Bonds, FII deposits, etc., declined by US $ 1 million over
the position in the previous quarter and stood at US $ 54,743 million as at end-September
2006. Even after offsetting the impact of redemption of India Millennium Deposits
(IMDs), external debt increased by US $ 266 million over the position a year ago.
India’s external debt increased by US $ 4,313 million from US $ 132,203
million as at end-June 2006 to US $ 136,516 million as at end-September 20061
. Non-debt liabilities (American Depository Receipts, Global Depository Receipts,
equities of banks held by non-residents and capital of foreign banks’ branches
in India) increased by US $ 3,288 million in September 2006 over June 2006. Foreign
currency liabilities towards residents increased to US $ 2,665 million as at end-September
2006 as compared with US $ 2,588 million in June 2006 and US $ 2,077 million a
year ago. Composition by Instruments
Major component-wise
international liabilities of banks in India as at end-September 2006 are presented
in Chart 2. ‘Deposits and loans’ accounted for
the largest share at 79.4 per cent of total international liabilities of banks
as at end-September 2006, however, it declined by 3.8 percentage points over the
share in the previous quarter due to considerable increase in the share of ‘other
international liabilities’ . The share of ‘own
issues of debt securities’ showed a decline over the position a year ago
due to redemption of IMDs in December 2005. The share of ‘other international
liabilities’ in total international liabilities increased by 3.8 and 8.1
percentage points compared to(Statement I) its share
in the previous quarter and a year ago, on account of significant increase in
banks’ equity holding by nonresidents. It may be noted that the considerable
increase in banks’ equity holding by non-residents during the quarter was
mainly due to significant increase in the value of equity shares of some bank(s).
About 72.0 per cent of the total international liabilities as at end-September
2006 accounted for by only three components of international liabilities, viz., 
NRE
Rupee deposits (32.2 per cent), Foreign Currency Borrowing (19.9 per cent) and
FCNR(B) deposits (19.7 per cent) (Statement I). While 69.2 per cent of FCNR(B)
deposits and 56.5 per cent of NRE Rupee deposits were mobilized from residents
of the three countries, viz., the US, the UK and UAE, about 68.9 per
cent of total foreign currency borrowings were made from the entities in the four
countries, viz., the US (37.4 per cent), the UK (14.9 per cent), Singapore
(9.9 per cent) and Germany (6.7 per cent) (Statement II).
The ‘loans and deposits’ accounted for the highest share of
92.2 per cent (Chart 3) in total international assets of
banks as at end-September 2006 registering a negligible decline of 0.2 percentage
point over the share in the previous quarter (Statement
I). The share of ‘holdings of international debt securities’
increased as compared to its share in the previous quarter as well as a year ago.
The share of ‘other international assets’, which includes investments
made by banks in foreign equities and capital supplied to and profits receivable
from foreign branches/ subsidiaries of Indian Banks, hovered around 6.4 per cent
in various quarters covering period from September 2005 to September 2006. About
88.2 per cent of the total international assets were composed of only three components
of international assets, viz., foreign currency loans to residents (37.6 per cent),
NOSTRO balances including placements abroad (28.7 per cent) and outstanding export
bills (21.9 per cent) as at end-September 2006 (Statement I). While, about 74.0
per cent of the total NOSTRO balances were concentrated only in three countries
[viz., the US (53.2 per cent), the UK (12.7 per cent) and Singapore (8.0 per cent)]
as at end-September 2006, more than 60.0 per cent of the total outstanding export
bills were spread over five countries [viz., the US (38.5 per cent), Hong Kong
(6.6 per cent), UAE (6.0 per cent), the UK (5.6 per cent) and Italy (4.5 per cent)]
(Statement III). Composition by Currency
Currency composition of international liabilities for all sectors as at end-September
2006 showed that the liabilities in Indian Rupee accounted for the maximum share
(49.4 per cent), followed by liabilities in the US dollar (39.0 per cent) and
Pound Sterling (6.9 per cent). The Euro denominated liabilities accounted for
a small share of 1.8 per cent during the quarter under reference (Chart
4, Table 3 and Statement IV).
The significant increase in the share of liabilities in Indian Rupee, over the
share a year ago, may be attributed to the redemption of IMDs in December 2005
and considerable increase in holding of equities of banks by non-residents.
With regard to currency composition of international assets for all sectors
as at end-September 2006, the US dollar denominated assets continued to account
for the maximum share (80.6 per cent), followed by Euro (4.9 per cent), Indian
Rupee (4.6 per cent), and Pound Sterling (3.5 per cent) (Chart 5, Table 3 and
Statement IV). 

Table 3: International Liabilities
and Assets | of
Banks - Currency Composition | (Rs.
crore) | Currency Name | Amount
Outstanding as at end | | September | June | September |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
International Liabilities | |
Total | 288,871 | 320,762 | 334,998 |
of which: | | | |
Indian Rupee | 122,828 | 153,754 | 165,500 |
| (42.5) | (47.9) | (49.4) |
US Dollar | 136,715 | 132,900 | 130,611 |
| (47.3) | (41.4) | (39.0) |
Pound Sterling | 15,081 | 18,584 | 23,057 |
| (5.2) | (5.8) | (6.9) |
| International
Assets | | Total | 135,203 | 154,204 | 162,991 |
of which: | | | |
US Dollar | 111,791 | 124,923 | 131,309 |
| (82.7) | (81.0) | (80.6) |
EURO | 5,536 | 7,643 | 8,008 |
| (4.1) | (5.0) | (4.9) |
Indian Rupee | 4,390 | 6,747 | 7,420 |
| (3.2) | (4.4) | (4.6) |
Pound Sterling | 6,448 | 5,519 | 5,782 |
| (4.8) | (3.6) | (3.5) |
Note :
1. Figures in brackets represent
percentages to total international assets
2. Data have been revised for previous
quarters. | 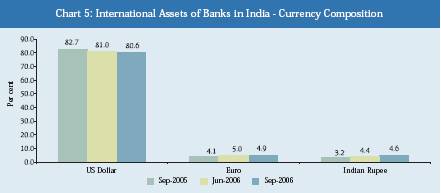
Composition
by Sector
The sectoral composition of international liabilities
of banks into “non-bank” sector increased over the period, correspondingly
the share of “bank” sector declined. The ‘non-bank’ sector
continued to hold major share and stood at 74.8 per cent as at end-September 2006
(Table 4).
As regards international assets, the
share of ‘bank’ sector increased by 3.5 percentage points as at end-September
2006 over the share in the previous quarter due to considerable increase in NOSTRO
balances and placements abroad and, correspondingly, the share of ‘non-bank’
sector declined. The currency and sector-wise composition of international liabilities
and assets in greater detail are presented in Statement
IV.
Composition by Country of Residence of Transacting Units
About 67.1 per cent of total international liabilities of banks were towards
the transacting units (bank and non-bank sector) of six countries, viz.,
the USA (29.4 per cent), the UK (15.5 per cent), UAE (8.2 per cent), Mauritius
(5.3 per cent), India (4.5 per cent) and Singapore (4.2 per cent) as at end-September
2006 (Chart 6 and Table 5). The share
of international liabilities towards the UK and Mauritius increased in contrast
to decline in share of the USA, UAE, India, and Singapore compared to their positions
in the previous quarter.
Table 4: International Liabilities
and Assets of | Banks
-Sector Composition | (Rs.
crore) | Sector | | Amount
Outstanding as at end | | | September | June | September |
| | 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
International Liabilities |
Total | | 288,871 | 320,762 | 334,998 |
of which: | | | |
Bank | | 83,986 | 87,727 | 84,275 |
| | (29.1) | (27.3) | (25.2) |
Non-Bank | 204,885 | 233,035 | 250,723 |
| | (70.9) | (72.7) | (74.8) |
International Assets |
Total | | 135,203 | 154,204 | 162,991 |
of which: | | | |
Bank | | 53,056 | 58,237 | 67,330 |
| | (39.2) | (37.8) | (41.3) |
Non-Bank | 82,147 | 95,967 | 95,661 |
| | (60.8) | (62.2) | (58.7) |
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent
percentages to
total international assets.
2. Data have been revised for
previous quarters. | 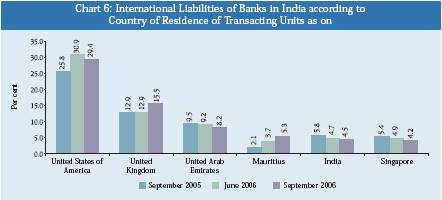
Table 5: International Liabilities
and Assetes of Banks in India according to Country of | Residence
of Transacting Units | (Rs.
crore) | Country of | Amount
Outstanding as at end | Country of | Amount
Outstanding as at end | Residence | | | | Residence | | | |
| September | June | September | | September | June | September |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2006 | | 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
International Liabilities | International
Assets | Total | | | | Total | | | |
International | | | | International | | | |
Liabilities | 288,871 | 320,762 | 334,998 | Assets | 135,203 | 154,204 | 162,991 |
of which: | | | | of
which: | | | |
United States of | 74,411 | 98,971 | 98,561 | India
| 61,703 | 62,779 | 61,751 |
America # | (25.8) | (30.9) | (29.4) | | (45.6) | (40.7) | (37.9) |
United | 37,333 | 41,507 | 52,066 | United
States | 31,421 | 37,423 | 42,585 |
Kingdom @ | (12.9) | (12.9) | (15.5) | of
America # | (23.2) | (24.3) | (26.1) |
United Arab | 27,342 | 29,495 | 27,364 | United | 9,778 | 10,039 | 11,747 |
Emirates | (9.5) | (9.2) | (8.2) | Kingdom
@ | (7.2) | (6.5) | (7.2) |
Mauritius | 5,996 | 11,826 | 17,869 | Singapore
| 3,480 | 5,080 | 6,675 |
| (2.1) | (3.7) | (5.3) | | (2.6) | (3.3) | (4.1) |
India | 16,795 | 14,974 | 14,925 | Hong
Kong | 3,742 | 4,330 | 4,622 |
| (5.8) | (4.7) | (4.5) | | (2.8) | (2.8) | (2.8) |
Singapore | 15,685 | 15,706 | 13,984 | | | | |
| (5.4) | (4.9) | (4.2) | | | | |
@: Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey.
#: Includes Miday Island and Wake Islands.
Note :
1. Figures in brackets
represent percentages to total international assets.
2. Data have been revised
for previous quarters. | In respect of international assets
of banks as at end-September 2006, 78.1 per cent of total international assets
concentrated in the five countries, viz., India (37.9 per cent), the
USA (26.1 per cent), the UK (7.2 per cent), Singapore (4.1 per cent) and Hong
Kong (2.8 per cent) (Chart 7 and Table
5). The details of international liabilities and assets of banks in India,
according to country of residence of transacting units, are presented in Statement
V. 
Composition
by Country of Incorporation of Reporting Bank
The classification
of international liabilities of banks according to their country of incorporation
revealed that the Indian Banks accounted for the maximum share at 80.7 per cent
as at end-September 2006, although it declined over the position a year ago. Banks
incorporated in other countries, namely, the USA, Hong Kong, the UK and Netherlands
had very low shares ranging between 2.0 per cent and 5.0 per cent (Table
6).
In the case of international assets, India accounted for the
highest share (81.3 per cent), followed by the USA (5.9 per cent), the UK (2.9
per cent), Germany (2.7 per cent), Netherlands (2.4 per cent) and Hong Kong (2.2
per cent). These countries, together, covered 97.4 per cent of total international
assets as at end-September 2006 (Table 6). Further details of international liabilities
and assets of banks according to their country of incorporation are presented
in Statement VI.
III.2 Consolidated Banking
Statistics (CBS)
International/Foreign Claims
The CBS provides country-wise (immediate country risk exposure), residual maturity-wise
and sector-wise classification of international claims of banks on countries other
than India. It also provides consolidated country risk exposure on an ultimate
risk basis, sector-wise classification of foreign claims (through on-balance-sheet
items) and international claims arising from derivatives, guarantees and credit
commitments. Data presented in the article are based on the data reported by branches
of banks in India and foreign branches of Indian Banks.
Table 6: International Liabilities
and Assets of | Banks
in India according to Country of | Incorporation
of Reporting Bank | (Rs.
crore) | Country of | Amount
Outstanding as at end | Incorporation | | | |
| September | June | September |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
International Liabilities |
Total | | | |
International | | | |
Liabilities | 288,871 | 320,762 | 334,998 |
of which: | | | |
India | 238,366 | 255,672 | 270,325 |
| (82.5) | (79.7) | (80.7) |
United States of | 12,610 | 16,803 | 16,770 |
America | (4.4) | (5.2) | (5.0) |
Hong Kong | 11,223 | 15,293 | 14,971 |
| (3.9) | (4.8) | (4.5) |
United Kingdom | 8,573 | 11,880 | 11,492 |
| (3.0) | (3.7) | (3.4) |
Netherlands | 5,787 | 7,388 | 6,793 |
| (2.0) | (2.3) | (2.0) |
International Assets |
| | | |
Total | | | |
International | | | |
Assets | 135,203 | 154,204 | 162,991 |
of which: | | | |
India | 110,886 | 124,497 | 132,535 |
| (82.0) | (80.7) | (81.3) |
United States of | 7,961 | 7,539 | 9,694 |
America | (5.9) | (4.9) | (5.9) |
United Kingdom | 2,790 | 5,707 | 4,786 |
| (2.1) | (3.7) | (2.9) |
Germany | 3,582 | 3,098 | 4,406 |
| (2.6) | (2.0) | (2.7) |
Netherlands | 4,768 | 4,871 | 3,937 |
| (3.5) | (3.2) | (2.4) |
Hong Kong | 2,572 | 4,266 | 3,551 |
| (1.9) | (2.8) | (2.2) |
Note :
1. Figures in brackets represent
percentages to total international assets.
2. Data have been revised for previous
quarters. | Exposure/Claims on Immediate Risk Basis
Consolidated international claims of banks, based on immediate risk basis,
on countries other than India as at end-September 2006, registered an increase
of Rs. 15,371 crore and Rs. 47,769 crore over the position in the previous quarter
and a year ago, respectively (Table 7).
Composition
by Country of Residence of Transacting Unit - Immediate risk basis
Consolidated international claims of banks, classified according to country of
immediate risk revealed that reporting banks’ claims on the USA accounted
for the largest share (25.4 per cent), followed by the UK (14.6 per cent) and
Singapore (6.2 per cent) as at end-September 2006 (Chart 8
and Table 7). The share of claims on the USA, the UK, Singapore,
and UAE increased while that of the Germany and Hong Kong declined over the position
in the previous quarter.
Composition by Residual Maturity-Immediate
Risk Basis
Consolidated international claims of banks on immediate
country risk basis, classified by their residual maturity, is presented in Table
8. The reporting banks continued to prefer short-term lending/ investment, since
the short-term claims (claims with residual maturity up to one year) accounted
for 75.1 per cent share of total international claims and the long-term claims
accounted for 24.2 per cent share as at end-September 2006 (Table
8). Also, the share of ‘short-term’ claims increased marginally
and, correspondingly, the share of ‘long-term’ claims declined over
the position in the previous quarter. The details of consolidated international
claims of banks according to residual maturity and country of immediate risk are
provided in.
Statement VII
Table 7: Consolidated International
Claims of Banks on Countries other than
India on Immediate Countr y Risk Basis |
Country | Amount
Outstanding as at end | | | September
2005 | June 2006 | | September
2006 | | | Rs.
crore+ | US $ | Rs.
crore+ | US $ | Rs.
crore+ | US $ | | | | million | million | | million |
Total Consolidated International | 66,919 | 15,202 | 99,317 | 21,572 | 114,688 | 24,973 |
Claims (excluding claims on India) | | | | | | |
of which: | | | | | | |
United States of America # | 18,409 | 4,182 | 24,283 | 5,274 | 29,152 | 6,348 |
| (27.5) | (27.5) | (24.4) | (24.4) | (25.4) | (25.4) |
United Kingdom@ | 10,133 | 2,302 | 12,106 | 2,629 | 16,745 | 3,646 |
| | (15.1) | (15.1) | (12.2) | (12.2) | (14.6) | (14.6) |
Singapore | 2,815 | 639 | 5,673 | 1,232 | 7,066 | 1,539 |
| | (4.2) | (4.2) | (5.7) | (5.7) | (6.2) | (6.2) |
United Arab Emirates | 3,402 | 773 | 3,824 | 831 | 5,100 | 1111 |
| | (5.1) | (5.1) | (3.9) | (3.9) | (4.4) | (4.4) |
Germany | 1,867 | 424 | 5,108 | 1,109 | 5,035 | 1,096 |
| | (2.8) | (2.8) | (5.1) | (5.1) | (4.4) | (4.4) |
Hong Kong | 5,125 | 1,164 | 4,999 | 1,086 | 4,944 | 1,077 |
| | (7.7) | (7.7) | (5.0) | (5.0) | (4.3) | (4.3) |
+ : 1 crore = 10 million. The FEDAI revaluation
rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at end-September 2005, June 2006, and September
2006 were Rs. 44.020, Rs 46.040 and Rs. 45.925 per US Dollar, respectively .
@ : Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # : Includes Miday Island and
Wake Islands.
Note : 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to the total
international claims.
2. Data have been revised for previous quarters. |

Table 8: Maturity-wise break-up
of Consolidated | International
Claims of Banks on Countries other than India on Immediate
Country Risk Basis |
(Rs. crore) |
Residual Maturity | AmountOutstanding
as at end | | | | September | June | September |
| | | 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
Short Term * | 53,028 | 74,013 | 86,175 |
| | | (79.2) | (74.5) | (75.1) |
Long Term ** | 12,899 | 24,227 | 27,796 |
| | | (19.3) | (24.4) | (24.2) |
Unallocated *** | 993 | 1,078 | 716 |
| | | (1.5) | (1.1) | (0.6) |
Total Consolidated | | | |
International | | | |
Claims (excluding | 66,919 | 99,317 | 114,688 |
claims on India) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
* : Claims with a residual maturity of up
to and including one year
** : Claims with a residual maturity of over one
year (excluding unallocated maturity)
*** : Residual Maturity “Unallocated”
comprises maturity not applicable for certain items (i.e., equities,
fixed assets, etc.) and maturity information not available.
Notes:
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
2. Data have been revised for previous quarters. | Composition
by Sector – Immediate Risk Basis
Sectoral classification of
consolidated international claims of banks on other countries, on immediate country
risk basis is presented in Table 9. The share of ‘bank’
sector increased, due to increase in NOSTRO balances and placements abroad,
by 2.6 percentage points as at end-September 2006 over the share in the previous
quarter and, correspondingly the share of ‘non-bank private’ sector
declined. The details of international claims of banks according to sector and
country of immediate risk are presented in Statement VII.
Table 9: Sector-wise Consolidated
International | Claims
of Banks on Countries other than India on Immediate Country Risk Basis |
(Rs. crore) |
Sector | Amount
Outstanding as on | | September | June | September |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2006 |
Bank | 25,251 | 40,580 | 49,932 |
| (37.7) | (40.9) | (43.5) |
Non-Bank | 1,396 | 732 | 840 |
Public Sector | (2.1) | (0.7) | (0.7) |
Non-Bank | 40,273 | 58,005 | 63,916 |
Private Sector | (60.2) | (58.4) | (55.7) |
Total Consolidated | 66,919 | 99,317 | 114,688 |
International Claims | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
(excluding claims | | | |
on India) | | | |
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent
percentages to total international claims.
2. Data have been revised for previous
quarters. | Exposure/Claims on Ultimate Risk Basis
Consolidated foreign claims (international claims of Indian Banks including
the claims of their foreign offices plus local claims in local currency of foreign
offices of Indian Banks) of domestic banks on ultimate risk basis increased from
Rs. 105,675 crore as at end-June 2006 to Rs. 118,295 crore as at end-September
2006 (Table 10). The consolidated contingent claims/exposure
of Indian Banks, on countries other than India, arising from derivatives, guarantees
and credit commitments as at end-September 2006 stood at Rs. 8,735 crore, Rs.
11,686 crore and Rs. 865 crore, respectively.
Table 10: Consolidated Foreign
Claims and Contingent Claims/Exposures arising from Derivatives,Guarantees and
Credit Commitments of Domestic Banks on Ultimate Risk Basis |
(Rs. crore) | Country
of | Consolidated Claim | | Country
of | Consolidated Claim |
Ultimate Risk | September
2005 | June
2006 | September
2006 | Ultimate
Risk | September
2005 | June
2006 | September
2006 | Total Foreign
Claims | Contingent Claims/Exposures
Arising from Guarantees | Total | 72,276 | 105,675 | 118,295 | Total | 9,172 | 10,424 | 11,686 |
of which: | | | | of
which: | | | |
United States | 19,016 | 22,307 | 26,162 | United
States | 2,555 | 2,684 | 3,558 |
of America # | (26.3) | (21.1) | (22.1) | of
America # | (27.9) | (25.7) | (30.4) |
United Kingdom @ | 12,846 | 11,814 | 15,932 | Germany
| 585 | 878 | 1,103 |
| (17.8) | (11.2) | (13.5) | | (6.4) | (8.4) | (9.4) |
Germany | 3,215 | 5,781 | 6,155 | China
| 688 | 1,133 | 815 |
| (4.4) | (5.5) | (5.2) | | (7.5) | (10.9) | (7.0) |
Canada | 1,706 | 4,849 | 6,044 | United
Arab Amirates | 801 | 559 | 749 |
| (2.4) | (4.6) | (5.1) | | (8.7) | (5.4) | (6.4) |
Singapore | 2,856 | 5,517 | 5,996 | United
Kingdom @ | 319 | 463 | 698 |
| (4.0) | (5.2) | (5.1) | | (3.5) | (4.4) | (6.0) |
Contingent Claims/
Exposures
Arising | Contingent Claims/
Exposures Arising from | from
Derivatives | Credit Commitments |
Total | 6,593 | 7,818 | 8,735 | Total | 639 | 729 | 865 |
of which: | | | | of
which: | | | |
France | 214 | 2,607 | 2,378 | United
States | 199 | 215 | 525 |
| (3.2) | (33.3) | (27.2) | of
America # | (31.1) | (29.5) | (60.7) |
United Kingdom @ | 898 | 1,322 | 1,516 | France
| 122 | 135 | 136 |
| (13.6) | (16.9) | (17.4) | | (19.1) | (18.5) | (15.7) |
Singapore | 235 | 181 | 1,358 | United
Kingdom @ | 66 | 114 | 52 |
| (3.6) | (2.3) | (15.5) | | (10.3) | (15.6) | (6.0) |
United States of | 1,754 | 684 | 605 | Singapore
| 39 | 60 | 48 |
America # | (22.2) | (8.7) | (6.9) | | (6.1) | (8.2) | (5.5) |
Germany | 1,407 | 737 | 565 | Canada
| 7 | 20 | 19 |
| (21.3) | (9.4) | (6.5) | | (1.1) | (2.7) | (2.2) |
@ : Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey.
# : Includes Miday Island and Wake Islands.
Note : Figures in brackets represent
percentages to total. | Composition by Country of Residence
of Transacting Units: Ultimate Risk Basis
Consolidated foreign claims
and claims arising from derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments of Indian
Banks, classified according to country of ultimate risk are presented in Table
10. About 51 per cent of total consolidated foreign claims of Indian Banks
were concentrated in five countries, viz., the USA (22.1 per cent), the
UK (13.5 per cent), Germany (5.2 per cent), Canada (5.1 per cent) and Singapore
(5.1 per cent). As regards consolidated international claims of Indian Banks arising
from derivatives, France had the maximum share at 27.2 per cent, followed by the
UK (17.4 per cent), Singapore (15.5 per cent) and the USA (6.9 per cent). In respect
of consolidated international claims of Indian Banks arising from guarantees,
the USA had the maximum share at 30.4 per cent, followed by Germany (9.4 per cent),
China (7.0 per cent) and UAE (6.4 per cent). About 90 per cent claims arising
from credit commitments were concentrated in five countries, viz., the
USA (60.7 per cent), France (15.7 per cent), the UK (6.0 per cent), Singapore
(5.5 per cent) and Canada (2.2 per cent).
III.3 Comparison of CBS
of the Countries Reporting Data to BIS
Vis-à-vis CBS
of India
A comparative position of CBS of India and the CBS of BIS reporting
countries as at end-September 2005 and 2006 has been presented in this section
covering three aspects, viz., (i) consolidated international/ foreign
claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on all other countries, (ii) consolidated
international/foreign claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on India
and (iii) international/foreign claims of Indian Banks on countries other than
India. It may be mentioned that the data published by the BIS relate to the consolidated
total international/foreign claims of all BIS reporting countries on other countries.
Further, the claims of India denote claims of Indian Banks’ branches/ offices,
operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India. Total
International/Foreign Claims-Immediate Risk Basis
Total foreign
claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on all other countries recorded
a growth of 18.9 per cent in September 2006 over September 2005 (Table
11). Also, total foreign claims of Indian Banks on other countries increased
by US $ 9.6 billion (51.3 per cent) during the same period. As regards the components
of ‘total foreign claims’, viz., ‘local claims
in local currencies’ and ‘international claims’, the share of
‘local claims in local currencies’ of banks in the BIS reporting countries
to total foreign claims declined marginally and correspondingly, the share of
total international claims increased at end-September 2006 as compared to their
respective share a year ago. In respect of claims of Indian Banks, the share of
international claims increased and, thus, the share of local claims in local currencies
declined.
International claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries
on India (i.e., India’s liability) stood at US $ 74.9 billion as
at end-September 2006, which was more by US $ 20.6 billion over the position a
year ago, whereas the international claims of Indian Banks on other countries
(i.e., India’s asset) stood at US $ 24.3 billion as at end-September
2006, which was more by US $ 9.1 billion over the position a year ago. As regards
‘total foreign claims’, the claims on India (US $ 120.3 billion) were
more than four times the claims of Indian Banks on other countries (US $ 28.3
billion). The considerable divergence could partly be attributed to the ‘local
claims in local currencies’ covering lending/investment of foreign banks’
offices in India (US $ 45.4 billion), which was significantly higher than the
‘local claims in local currencies’ of Indian Banks’ foreign
offices (US $ 4.0 billion).
Table 11: Claims of BIS Reporting
Banks on India & other Countries and Indian Banks' Claim on other Countries
- Immediate Country Risk Basis | (US
$ billion) | Claims | Claims
of BIS Reporting Countries' Banks on all other Countries | Claims
of BIS Reporting Countries' Banks on India | Claims
of Indian Banks on Countries other than India # | | September
2005 | September 2006 | September
2005 | September 2006 | September
2005 | September 2006 |
(a) Total International Claims | 14,481.9 | 17,230.7 | 54.3 | 74.9 | 15.2 | 24.3 |
| (67.3) | (67.4) | (59.5) | (62.3) | (81.3) | (85.9) |
(b) Local Claims in Local Currencies | 7,039.9 | 8,351.0 | 37.0 | 45.4 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
| (32.7) | (32.6) | (40.5) | (37.7) | (18.7) | (14.1) |
(c) Total Foreign Claims (a+b) | 21,521.8 | 25,581.7 | 91.3 | 120.3 | 18.7 | 28.3 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
# : Claims of Indian Banks’ branches/offices
operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken
from the data supplied to the BIS.
Note :
Figures in brackets represent
percentages to total foreign claims.
Source :
BIS International Consolidated
Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) updated till January 24, 2007. |
International Claims-by Residual Maturity and Sector
Maturity-wise classification of international claims of banks in the BIS reporting
countries on all other countries revealed that the share of ‘long-term’
as well as ‘short-term’ claims declined marginally as at end-September
2006 compared to their respective shares a year ago due to increase in claims
in unallocated category. The ndian Banks preferred ‘short-term’ lending/
investment as at end-September 2006. However, the share of ‘short-term’
claims declined and the share of ‘long-term’ claims increased.
Maturity pattern of international claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries
on India and that of international claims of Indian Banks on other countries revealed
that the short-term claims on India (US $ 39.7 billion) were more than double
the short-term claims of Indian Banks on other countries (US $ 18.7 billion) at
end-September 2006 (Table 12). Like wise, the long-term
claims on India (US $ 20.4 billion) were more than three times the long-term claims
of Indian Banks on other countries (US $ 5.4 billion). The short-term claims of
banks in the BIS reporting countries on India increased by US $ 10.2 billion in
September 2006 over the position a year ago compared to an increase of US $ 6.7
billion in short-term claims of Indian Banks on countries other than India during
the same period.
Table 12: International Claims
of BIS Reporting Banks vis-à-vis Indian Banks -by Maturity and
Sector | (US $
billion) | Maturity/Sector | Claims
of BIS Reporting Countries on all other Countries | Claims
of BIS Reporting Countries on India | Claims
of Indian Banks on Countries other than India # | | | | September
2005 | September 2006 | September
2005 | September 2006 | September
2005 | September 2006 |
Total International Claim | 14,481.9 | 17,230.7 | 54.3 | 74.9 | 15.2 | 24.3 |
of which: | | | | | | | |
Maturity | Short
Term * | 7,930.7 | 9,288.9 | 29.5 | 39.7 | 12.0 | 18.7 |
| | | (54.8) | (53.9) | (54.4) | (53.0) | (78.9) | (77.0) |
| | Long
Term ** | 4,391.9 | 5,181.8 | 15.8 | 20.4 | 2.9 | 5.4 |
| | | (30.3) | (30.1) | (29.1) | (27.3) | (19.1) | (22.2) |
Sector $ | Bank | 6,806.6 | 7,938.7 | 19.0 | 22.2 | 5.7 | 10.5 |
| | | (47.0) | (46.1) | (35.0) | (29.6) | (37.5) | (43.2) |
| | Non-Bank | 2,084.6 | 2,216.1 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| | Public | (14.4) | (12.9) | (8.7) | (6.2) | (2.0) | (0.8) |
| | Non-Bank | 5,383.8 | 6,850.6 | 29.0 | 46.2 | 9.1 | 13.5 |
| | Private | (37.2) | (39.8) | (53.4) | (61.7) | (59.9) | (55.6) |
# : Claims of Indian Banks’ branches/offices
operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken
from the data supplied to the BIS.
* : Claims with a residual maturity of
up to and including one year.
** : Claims with a maturity of over one year
(excluding unallocated maturity).
$ : Excluding unallocated sector.
Note
: Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
Source : BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) updated
till January 24, 2007. |
Sector-wise composition of international claims of banks in the BIS reporting
countries on all other countries as at end-September 2006 showed that the share
of ‘non-bank private’ sector increased by 2.6 percentage points over
the share a year ago, while the share of ‘bank’ and ‘non-bank
public’ sectors declined. In respect of Indian Banks’ international
claims on countries other than India, the shares of ‘bank’ sector
increased, and the share of ‘non-bank public’ and ‘non-bank
private’ sectors declined.
Comparative position of sector-wise
classification showed that the share of claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries
on India in the ‘non-bank private’ sector increased while the share
declined for ‘bank’ and ‘non bank public’ sectors in September
2006 over September 2005. International Claims-by Country of Incorporation
of Reporting Banks
International claims of banks in the BIS reporting
countries on all other countries classified according to the country of incorporation
of the bank as at end-September 2005 and 2006 are presented in . The banks incorporated
in Germany continued to account for the maximum share at 20.2 per cent, followed
by banks incorTable 13porated in Japan (11.2 per cent),
France (11.0 per cent), the UK (10.7 per cent), and Netherlands (7.6 per cent).
However, the share of banks incorporated in Germany declined in September 2006
over their share a year ago. The Indian Banks’ share in total international
claims, though increased, was negligible at 0.2 per cent as at end-September 2006.
Table 13: International Claims
of | BIS Reporting
Banks on all other Countries - by Country of Incorporation |
(US $ billion) |
Country of | International
Claims on | Incorporation | all
other Countries | | September | September |
| 2005 | 2006 |
Total International Claims | 11,579.2 | 13,541.6 |
of which: | | |
Germany | 2,541.0 | 2,734.7 |
| (21.9) | (20.2) |
Japan | 1,371.3 | 1,515.3 |
| (11.8) | (11.2) |
France | 1,170.9 | 1,490.1 |
| (10.1) | (11.0) |
United Kingdom | 1,220.4 | 1,448.7 |
| (10.5) | (10.7) |
Netherlands | 866.1 | 1,031.0 |
| (7.5) | (7.6) |
Belgium | 604.6 | 702.0 |
| (5.2) | (5.2) |
United States | 569.3 | 788.7 |
| (4.9) | (5.8) |
India # | 15.2 | 24.3 |
| (0.1) | (0.2) |
#: Claims of Indian Banks’ branches/offices
operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken
from the data supplied to the BIS.
Note : Figures in brackets represent percentages
to total international claims.
Source : BIS International Consolidated Banking
Statistics
(www.bis.org) updated till January 24, 2007. | Such
claims of banks on India according to their country of incorporation revealed
that the banks incorporated in five countries, viz., the USA, Germany,
the UK, Japan, Netherlands and France accounted for 74.7 per cent share in aggregate
as at end-September 2006. While the shares of claims of banks incorporated in
the USA and Japan increased, the shares of banks incorporated in Germany, the
UK, Netherlands and France declined in September 2006 over September 2005
(Table 14).
Table 14: International Claims
of BIS Reporting | Banks
on India - by Country of Incorporation | | | (US
$ billion) | Country
of Incorporation | International
Claims on India | | | September2005 | September2006 |
Total International Claim | 42.8 | 61.3 |
of which: | | |
| | | |
United States | 8.1 | 14.3 |
| | (18.8) | (23.4) |
Germany | | 7.1 | 8.6 |
| | (16.7) | (14.0) |
Uk Excl. Islands | 6.1 | 7.3 |
| | (14.3) | (12.0) |
Japan | | 4.3 | 6.3 |
| | (10.0) | (10.3) |
Netherlands | 4.4 | 5.1 |
| | (10.4) | (8.3) |
France | | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| | (9.1) | (6.7) |
Note :
1. The data on international
claims on India of banks incorporated in Canada and Ireland are masked by the
BIS.
2. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
Source :
BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org)
updated till January 24, 2007. | Foreign Claims: Ultimate
Risk Basis
Total foreign claims, on ultimate risk basis, of banks
in the BIS reporting countries on all other countries stood at US $ 21,107.9 billion
as at end-September 2006, of which 53.2 per cent claims were on ‘non-bank
private’ sector (Table 15). The foreign claims of
banks in the BIS reporting countries on India stood at US $ 105.6 billion as at
end-September 2006, which was more than four times the foreign claims of Indian
Banks on other countries (US $ 25.8 billion).
Table 15: Consolidated Foreign
Claims of BIS Reporting Banks on India & other Countries |
and Indian Banks' Claim on other
Countries: Ultimate Risk Basis | (US
$ billion) | Claims | Claims
of BIS Reporting | Claims
of BIS Reporting | Claims
of Indian Banks | | Countries'
Banks on | Countries' Banks | on
Countries other than | | all
other Countries ## | on India | India
# | | September | September | September | September | September | September |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | 2006 |
(a) Total Foreign Claims
of
which: | 17,893.2 | 21,107.9 | 80.5 | 105.6 | 16.4 | 25.8 |
| Banks | 5,145.6 | 5,978.5 | 17.6 | 21.2 | 8.1 | 14.3 |
| | (28.8) | (28.3) | (21.8) | (20.1) | (49.4) | (55.4) |
Sector | Non-Bank
Public | 3,316.3 | 3,708.8 | 7.2 | 11.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| | (18.5) | (17.6) | (8.9) | (10.9) | (2.4) | (1.2) |
| Non-Bank Private | 8,739.4 | 11,226.4 | 43.0 | 72.6 | 7.9 | 11.1 |
| | (48.8) | (53.2) | (53.5) | (68.8) | (48.2) | (43.0) |
(b) Other Exposures | | | | | | |
Derivatives | 2,244.5 | 2,132.4 | 2.6 | 4.9 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
Guarantees | 1,480.9 | 3,564.1 | 6.7 | 11.7 | 2.1 | 2.5 |
Credit Commitments | 3,756.4 | 3,664.5 | 7.4 | 9.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
# : Claims of Indian banks’ branches/offices
operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken
from the data supplied to the BIS.
## : Out of thirty countries submitting
CBS on immediate risk basis, twenty four countries submitted CBS on ultimate risk
basis to the BIS.
Note : Figures in brackets represent percentages to total
foreign claims.
Source :
BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics
(www.bis.org) updated till January 24, 2007. | IV. Summary
The international liabilities as well as the international assets of banks
increased as at end-September 2006 over the previous quarter. However, international
liabilities of banks were almost double than their international assets (Chart
1). While international liabilities of banks increased by Rs. 14,236 crore
(4.4 per cent), due to considerable increase in equities of banks held by non-residents
and ADRs/GDRs, as at end-September 2006 over the position in the previous quarter,
the international assets of banks increased by Rs. 8,787 crore (5.7 per cent)
during the same period, mainly due to sizeable increase in NOSTRO balances
held abroad and loans extended to non-residents. About 72.0 per cent of
the total international liabilities as at end-September 2006 accounted for by
NRE Rupee deposits, Foreign Currency Borrowing and FCNR(B) deposits whereas about
88.2 per cent of the total international assets were comprised of foreign currency
loans to residents, NOSTRO balances including placements abroad and outstanding
export bills (Statement I). While 69.2 per cent of the
FCNR(B) and 56.5 per cent of NRE Rupee deposits were mobilized from residents
of three countries, viz., the US, the UK and UAE, about 68.9 per cent
of total foreign currency borrowings were made from the entities of four countries,
viz., the US, the UK, Singapore and Germany (Statement
II). 74 per cent of the total NOSTRO balances were concentrated only in three
countries (viz., the US, the UK and the Singapore). The outstanding export
bills spread over 5 countries (viz., the US, Hong Kong, UAE, the UK,
and Italy) accounted for 61.2 per cent to total outstanding export bills as at
end-September 2006 (Statement III).
The international
liabilities of banks, as at end-September 2006, were mainly denominated in two
currencies (viz., Indian Rupee (49.4 per cent) and US dollar (39.0 per
cent)), and 67.1 per cent of their liabilities were spread over six countries,
viz., the USA, the UK, UAE, Mauritius, India and Singapore. More than
70 per cent liabilities were towards ‘non-bank’ sector. As regards
international assets of banks as at end-September 2006, about 80 per cent were
denominated in the US dollar. Also, more than three-fourths of the international
assets were accounted for by five countries, viz., India, the US, the
UK, Singapore and Hong Kong. A major part (58.7 per cent) of the international
assets were with ‘non bank’ sector.
Consolidated international
claims, based on immediate risk basis, of banks on countries other than India
as at end- September 2006 registered an increase of Rs. 15,371 crore over the
position in the previous quarter. About 75.1 per cent of these claims were of
short-term maturity (residual maturity of less than one year) and 59.3 per cent
claims were on the USA, the UK, Singapore, UAE, Germany and Hong Kong. Further,
while 55.7 per cent claims were on ‘non-bank private’ sector entities,
43.5 per cent claims were on ‘bank’ sector.
Consolidated
foreign claims of Indian Banks on ultimate risk basis stood at Rs. 1,18,295 crore
as at end-September 2006. The consolidated contingent claims/ exposures of Indian
Banks arising from derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments stood at Rs.
8,735 crore, Rs. 11,686 crore and Rs. 865 crore, respectively.
International
claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on India (i.e., India’s liability)
stood at US $ 74.9 billion as at end-September 2006, which was higher by US $
20.6 billion over the position a year ago, whereas the international claims of
Indian Banks on other countries (i.e., India’s asset) stood at US $ 24.3
billion as at end-September 2006, registering a rise of US $ 9.1 billion during
2005-06.
Statement I: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Type | (Based
on LBS Statements) | (Rs.
crore) | Liability/Asset Category | International
Liabilities | | | | Amount
Outstanding as at end of | | | | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | 1. | Deposits
and Loans | 2,26,797 | 2,34,927 | 2,46,246 | 2,66,759 | 2,66,043 |
| | | (78.5) | (83.1) | (80.3) | (83.2) | (79.4) |
| (a) | Foreign
Currency Non-resident Bank [FCNR(B)] Scheme | 51,781 | 53,789 | 58,110 | 63,886 | 65,931 |
| | | (17.9) | (19.0) | (19.0) | (19.9) | (19.7) |
| (b) | Resident
Foreign Currency (RFC) A/Cs | 1,402 | 1,316 | 1,580 | 1,702 | 1,517 |
| | | (0.5) | (0.5) | (0.5) | (0.5) | (0.5) |
| (c) | Exchange
Earners Foreign Currency (EEFC) A/Cs | 5,993 | 6,671 | 6,013 | 6,936 | 7,210 |
| | | (2.1) | (2.4) | (2.0) | (2.2) | (2.2) |
| (d) | Other
foreign Currency Deposits (including | 1,748 | 1,826 | 2,646 | 3,276 | 3,514 |
| | Inter-bank
Foreign Currency deposits) | (0.6) | (0.6) | (0.9) | (1.0) | (1.0) |
| (e) | Foreign
Currency Borrowing (Inter-bank borrowing | | | | | |
| | in
India and from abroad, external commercial | 59,323 | 60,021 | 63,722 | 70,407 | 66,533 |
| | borrowings
of banks) | (20.5) | (21.2) | (20.8) | (21.9) | (19.9) |
| (f) | VOSTRO
balances and balances in exchange houses | 2,150 | 2,151 | 1,839 | 1,644 | 1,250 |
| | and
in term deposits | (0.7) | (0.8) | (0.6) | (0.5) | (0.4) |
| (g) | Non-resident
External Rupee(NRE)Accounts | 95,033 | 98,461 | 100,310 | 105,982 | 107,846 |
| | | (32.9) | (34.8) | (32.7) | (33.0) | (32.2) |
| (h) | Non-Resident
Ordinary (NRO) Rupee Accounts | 5,791 | 5,765 | 5,449 | 6,013 | 5,967 |
| | | (2.0) | (2.0) | (1.8) | (1.9) | (1.8) |
| (i) | Embassy
Accounts | 144 | 149 | 126 | 183 | 203 |
| | | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
| (j) | Foreign
Institutional Investors’ (FII) Accounts | 3,378 | 4,722 | 6,421 | 6,702 | 6,055 |
| | | (1.2) | (1.7) | (2.1) | (2.1) | (1.8) |
| (k) | ESCROW
A/Cs | 54 | 55 | 32 | 29 | 16 |
| | | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
2. | Own Issues
of International Securities | 30,293 | 4,458 | 4,856 | 5,063 | 5,040 |
| | | (10.5) | (1.6) | (1.6) | (1.6) | (1.5) |
| (a) | Bonds
(including IMDs) | 30,288 | 4,458 | 4,410 | 4,603 | 4,581 |
| | | (10.5) | (1.6) | (1.4) | (1.4) | (1.4) |
| (b) | Floating
Rate Notes (FRN) | 4 | — | — | — | — |
| | | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
| (c) | Other
Own Issues of International Debt Securities | — | — | 446 | 460 | 459 |
| | | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
3. | Other International
Liabilities | 31,781 | 43,389 | 55,506 | 48,939 | 63,915 |
| | | (11.0) | (15.3) | (18.1) | (15.3) | (19.1) |
| (a) | ADRs/GDRs | 13,113 | 16,027 | 14,835 | 13,092 | 17,617 |
| | | (4.5) | (5.7) | (4.8) | (4.1) | (5.3) |
| (b) | Equities
of Banks held by Non-residents | 8,835 | 16,985 | 28,438 | 23,206 | 33,362 |
| | | (3.1) | (6.0) | (9.3) | (7.2) | (10.0) |
| (c) | Capital/Remittable
Profits of Foreign Banks in India | 9,833 | 10,378 | 12,233 | 12,640 | 12,936 |
| | and
Other Unclassified International Liabilities | (3.4) | (3.7) | (4.0) | (3.9) | (3.9) |
| | | | | | | |
Total International Liabilities + | 2,88,871 | 2,82,775 | 3,06,609 | 3,20,762 | 3,34,998 |
| | | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
Statement I: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Type | (Based
on LBS Statements) (Concld.) | (Rs.
crore) | Liability/Asset Category | International
Assets | | | | Amount
Outstanding as at end of | | | | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | 1. | Loans
and Deposits | 1,25,236 | 1,36,017 | 1,46,014 | 1,42,539 | 1,50,311 |
| | | (92.6) | (92.8) | (92.3) | (92.4) | (92.2) |
| (a) | Loans
to Non-residents (includes Rupee loans | | | | | |
| | and
Foreign Currency (FC) Loans out of | 4,504 | 4,734 | 6,270 | 5,754 | 6,079 |
| | Non-resident
Deposits) | (3.3) | (3.2) | (4.0) | (3.7) | (3.7) |
| (b) | FC
Loans to Residents (incl. loans out of | | | | | |
| | FCNR(B)
deposits, PCFCs, FC lending to & FC | 61,292 | 61,644 | 63,231 | 62,440 | 61,330 |
| | Deposits
with Banks in India, etc., | (45.3) | (42.1) | (40.0) | (40.5) | (37.6) |
| (c) | Outstanding
Export Bills drawn on | 26,566 | 28,124 | 31,556 | 34,994 | 35,644 |
| | Non-residents
by Residents | (19.6) | (19.2) | (19.9) | (22.7) | (21.9) |
| (d) | Foreign
Currency /TTs, etc., in hand | 216 | 335 | 443 | 381 | 405 |
| | | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.2) | (0.2) |
| (e) | NOSTRO
Balances including Balances in Term | | | | | |
| | Deposits
with Non-resident Banks (includes | 32,658 | 41,181 | 44,515 | 38,970 | 46,853 |
| | FCNR
Funds Held Abroad) | (24.2) | (28.1) | (28.1) | (25.3) | (28.7) |
2. | Holdings of
Debt Securities | 1,260 | 1,498 | 2,079 | 1,927 | 2,206 |
| | | (0.9) | (1.0) | (1.3) | (1.2) | (1.4) |
| (a) | Investment
in Foreign Government Securities | 117 | 49 | 72 | 76 | 77 |
| | (including
Treasury Bills) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
| (b) | Investment
in Other Debt Securities | 1,143 | 1,449 | 2,007 | 1,850 | 2,128 |
| | | (0.8) | (1.0) | (1.3) | (1.2) | (1.3) |
3. | Other International
Assets | 8,707 | 9,022 | 10,109 | 9,738 | 10,474 |
| | | (6.4) | (6.2) | (6.4) | (6.3) | (6.4) |
| (a) | Investments
in Equities Abroad | 1,362 | 1,607 | 1,975 | 1,286 | 1,522 |
| | | (1.0) | (1.1) | (1.2) | (0.8) | (0.9) |
| (b) | Capital
supplied to and receivable profits from | | | | | |
| | foreign
branches of Indian banks and other | 7,345 | 7,415 | 8,134 | 8,453 | 8,952 |
| | Unclassified
International Assets | (5.4) | (5.1) | (5.1) | (5.5) | (5.5) |
| | | | | | | |
Total International Assets + | 1,35,203 | 1,46,537 | 1,58,201 | 1,54,204 | 1,62,991 |
| | | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
+ : In view of the incomplete data coverage
from all the branches, the data reported
under the LBS are not strictly comparable
with those capturing data from all the branches.
‘—’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international
liabilities/assets.
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off .
3. Data
have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters
ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement II: Country-wise Breakup of Major
Component of International Liabilities of Banks | (Based
on LBS Statements) | (Rs.
crore) | Country | Major | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | | Components | | | | | | | | | | |
Bahrain | FCNR(B) | 495 | (1.0) | 418 | (0.8) | 462 | (0.8) | 617 | (1.0) | 752 | (1.1) |
| Borrowings | 2,138 | (3.6) | 2,674 | (4.5) | 2,165 | (3.4) | 2,465 | (3.5) | 1,969 | (3.0) |
| NRE Deposits | 1,265 | (1.3) | 1,480 | (1.5) | 1,586 | (1.6) | 2,272 | (2.1) | 1,950 | (1.8) |
| Total | 4,462 | (1.5) | 4,842 | (1.7) | 4,432 | (1.4) | 5,588 | (1.7) | 4,945 | (1.5) |
Canada | FCNR(B) | 952 | (1.8) | 1,105 | (2.1) | 957 | (1.6) | 1,344 | (2.1) | 1,374 | (2.1) |
| Borrowings | 95 | (0.2) | 104 | (0.2) | 119 | (0.2) | 115 | (0.2) | 107 | (0.2) |
| NRE Deposits | 1,296 | (1.4) | 1,445 | (1.5) | 1,421 | (1.4) | 1,263 | (1.2) | 1,597 | (1.5) |
| Total | 3,258 | (1.1) | 3,272 | (1.2) | 3,181 | (1.0) | 3,550 | (1.1) | 4,044 | (1.2) |
France | FCNR(B) | 142 | (0.3) | 196 | (0.4) | 173 | (0.3) | 176 | (0.3) | 164 | (0.2) |
| Borrowings | 853 | (1.4) | 749 | (1.2) | 659 | (1.0) | 563 | (0.8) | 596 | (0.9) |
| NRE Deposits | 316 | (0.3) | 365 | (0.4) | 182 | (0.2) | 272 | (0.3) | 150 | (0.1) |
| Total | 2,426 | (0.8) | 2,744 | (1.0) | 2,576 | (0.8) | 2,475 | (0.8) | 2,732 | (0.8) |
Germany | FCNR(B) | 735 | (1.4) | 844 | (1.6) | 878 | (1.5) | 839 | (1.3) | 922 | (1.4) |
| Borrowings | 4,205 | (7.1) | 3,649 | (6.1) | 3,653 | (5.7) | 4,294 | (6.1) | 4,449 | (6.7) |
| NRE Deposits | 630 | (0.7) | 863 | (0.9) | 849 | (0.8) | 789 | (0.7) | 905 | (0.8) |
| Total | 6,901 | (2.4) | 7,251 | (2.6) | 6,933 | (2.3) | 7,408 | (2.3) | 7,725 | (2.3) |
Hong Kong | FCNR(B) | 833 | (1.6) | 1,054 | (2.0) | 751 | (1.3) | 947 | (1.5) | 944 | (1.4) |
| Borrowings | 2,675 | (4.5) | 1,719 | (2.9) | 1,532 | (2.4) | 2,366 | (3.4) | 2,075 | (3.1) |
| NRE Deposits | 1,470 | (1.5) | 1,707 | (1.7) | 1,481 | (1.5) | 1,173 | (1.1) | 1,197 | (1.1) |
| Total | 10,933 | (3.8) | 8,808 | (3.1) | 8,131 | (2.7) | 8,930 | (2.8) | 9,567 | (2.9) |
India | FCNR(B) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) |
| Borrowings | 3,675 | (6.2) | 5,412 | (9.0) | 3,957 | (6.2) | 4,671 | (6.6) | 4,996 | (7.5) |
| NRE Deposits | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) |
| Total | 16,795 | (5.8) | 14,202 | (5.0) | 12,518 | (4.1) | 14,974 | (4.7) | 14,925 | (4.5) |
Japan | FCNR(B) | 471 | (0.9) | 415 | (0.8) | 293 | (0.5) | 196 | (0.3) | 240 | (0.4) |
| Borrowings | 1,978 | (3.3) | 1,774 | (3.0) | 1,959 | (3.1) | 1,044 | (1.5) | 1,183 | (1.8) |
| NRE Deposits | 784 | (0.8) | 551 | (0.6) | 791 | (0.8) | 533 | (0.5) | 532 | (0.5) |
| Total | 4,130 | (1.4) | 3,872 | (1.4) | 4,671 | (1.5) | 2,649 | (0.8) | 3,836 | (1.1) |
Kenya | FCNR(B) | 550 | (1.1) | 904 | (1.7) | 752 | (1.3) | 1,016 | (1.6) | 1,131 | (1.7) |
| Borrowings | 20 | (—) | 70 | (0.1) | 52 | (0.1) | 19 | (—) | 49 | (0.1) |
| NRE Deposits | 597 | (0.6) | 858 | (0.9) | 1,090 | (1.1) | 886 | (0.8) | 1,369 | (1.3) |
| Total | 1,278 | (0.4) | 1,861 | (0.7) | 1,928 | (0.6) | 1,951 | (0.6) | 2,593 | (0.8) |
Kuwait | FCNR(B) | 1,240 | (2.4) | 1,463 | (2.7) | 1,696 | (2.9) | 1,900 | (3.0) | 1,942 | (2.9) |
| Borrowings | 97 | (0.2) | 90 | (0.1) | — | (—) | 17 | (—) | 44 | (0.1) |
| NRE Deposits | 4,074 | (4.3) | 4,713 | (4.8) | 5,039 | (5.0) | 3,937 | (3.7) | 3,829 | (3.6) |
| Total | 6,183 | (2.1) | 6,651 | (2.4) | 7,011 | (2.3) | 6,113 | (1.9) | 6,108 | (1.8) |
Mauritius | FCNR(B) | 19 | (—) | 18 | (—) | 6 | (—) | 8 | (—) | 12 | (—) |
| Borrowings | 174 | (0.3) | 121 | (0.2) | 135 | (0.2) | 111 | (0.2) | 236 | (0.4) |
| NRE Deposits | 67 | (0.1) | 51 | (0.1) | 67 | (0.1) | 61 | (0.1) | 52 | (—) |
| Total | 5,996 | (2.1) | 9,645 | (3.4) | 12,676 | (4.1) | 11,826 | (3.7) | 17,869 | (5.3) |
Netherlands | FCNR(B) | 119 | (0.2) | 86 | (0.2) | 78 | (0.1) | 93 | (0.1) | 114 | (0.2) |
| Borrowings | 3,202 | (5.4) | 2,632 | (4.4) | 3,121 | (4.9) | 4,095 | (5.8) | 3,083 | (4.6) |
| NRE Deposits | 202 | (0.2) | 192 | (0.2) | 167 | (0.2) | 178 | (0.2) | 206 | (0.2) |
| Total | 5,681 | (2.0) | 4,985 | (1.8) | 5,836 | (1.9) | 6,956 | (2.2) | 6,224 | (1.9) |
Statement II:
Country-wise breakup of Major Components of International Liabilities of Banks |
(Based on LBS
Statements) (Concld.) | (Rs.
crore) | Country | | Major
Components | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Oman | | FCNR(B) | 769 | (1.5) | 729 | (1.4) | 712 | (1.2) | 1,246 | (2.0) | 1,030 | (1.6) |
| | Borrowings | 105 | (0.2) | 55 | (0.1) | 1,086 | (1.7) | 704 | (1.0) | 34 | (0.1) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 3,523 | (3.7) | 2,972 | (3.0) | 2,866 | (2.9) | 3,332 | (3.1) | 2,871 | (2.7) |
| | Total | 5,184 | (1.8) | 4,050 | (1.4) | 4,851 | (1.6) | 5,463 | (1.7) | 4,151 | (1.2) |
Qatar | | FCNR(B) | 299 | (0.6) | 348 | (0.6) | 441 | (0.8) | 493 | (0.8) | 344 | (0.5) |
| | Borrowings | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | 129 | (0.2) | — | (—) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 1,380 | (1.5) | 1,750 | (1.8) | 1,587 | (1.6) | 1,950 | (1.8) | 1,689 | (1.6) |
| | Total | 1,994 | (0.7) | 2,249 | (0.8) | 2,191 | (0.7) | 2,771 | (0.9) | 2,175 | (0.6) |
Saudi Arabia | FCNR(B) | 1,898 | (3.7) | 1,704 | (3.2) | 1,298 | (2.2) | 1,895 | (3.0) | 1,447 | (2.2) |
| | Borrowings | 132 | (0.2) | — | (—) | 182 | (0.3) | 421 | (0.6) | 189 | (0.3) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 5,772 | (6.1) | 6,307 | (6.4) | 7,546 | (7.5) | 7,023 | (6.6) | 7,198 | (6.7) |
| | Total | 8,572 | (3.0) | 8,620 | (3.0) | 9,487 | (3.1) | 9,772 | (3.0) | 9,156 | (2.7) |
Singapore | FCNR(B) | 678 | (1.3) | 937 | (1.7) | 426 | (0.7) | 710 | (1.1) | 345 | (0.5) |
| | Borrowings | 7,375 | (12.4) | 8,263 | (13.8) | 8,611 | (13.5) | 8,514 | (12.1) | 6,600 | (9.9) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 2,728 | (2.9) | 1,480 | (1.5) | 1,819 | (1.8) | 1,456 | (1.4) | 1,518 | (1.4) |
| | Total | 15,685 | (5.4) | 14,843 | (5.2) | 15,658 | (5.1) | 15,706 | (4.9) | 13,984 | (4.2) |
Sri Lanka | FCNR(B) | 728 | (1.4) | 52 | (0.1) | 38 | (0.1) | 33 | (0.1) | 40 | (0.1) |
| | Borrowings | 2 | (—) | — | (—) | 49 | (0.1) | — | (—) | 11 | (—) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 1,309 | (1.4) | 864 | (0.9) | 915 | (0.9) | 890 | (0.8) | 896 | (0.8) |
| | Total | 2,116 | (0.7) | 988 | (0.3) | 1,110 | (0.4) | 1,016 | (0.3) | 1,026 | (0.3) |
United Arab Emirates | FCNR(B) | 3,981 | (7.7) | 4,361 | (8.1) | 6,486 | (11.2) | 8,479 | (13.3) | 8,303 | (12.6) |
| | Borrowings | 231 | (0.4) | 714 | (1.2) | 748 | (1.2) | 175 | (0.2) | 202 | (0.3) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 13,419 | (14.1) | 16,264 | (16.5) | 16,225 | (16.2) | 19,259 | (18.2) | 17,382 | (16.1) |
| | Total | 27,342 | (9.5) | 22,881 | (8.1) | 25,018 | (8.2) | 29,495 | (9.2) | 27,364 | (8.2) |
United Kingdom | FCNR(B) | 10,104 | (19.5) | 11,258 | (20.9) | 12,999 | (22.4) | 14,128 | (22.1) | 18,069 | (27.4) |
| | Borrowings | 8,417 | (14.2) | 8,604 | (14.3) | 8,936 | (14.0) | 9,344 | (13.3) | 9,939 | (14.9) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 8,267 | (8.7) | 8,159 | (8.3) | 9,901 | (9.9) | 11,018 | (10.4) | 14,304 | (13.3) |
| | Total | 37,333 | (12.9) | 35,871 | (12.7) | 40,961 | (13.4) | 41,507 | (12.9) | 52,066 | (15.5) |
United States | FCNR(B) | 18,215 | (35.2) | 18,192 | (33.8) | 20,015 | (34.4) | 19,579 | (30.6) | 19,240 | (29.2) |
| | Borrowings | 19,712 | (33.2) | 18,715 | (31.2) | 21,509 | (33.8) | 26,115 | (37.1) | 24,864 | (37.4) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 20,995 | (22.1) | 26,293 | (26.7) | 25,120 | (25.0) | 28,629 | (27.0) | 29,180 | (27.1) |
| | Total | 74,411 | (25.8) | 82,110 | (29.0) | 84,301 | (27.5) | 98,971 | (30.9) | 98,561 | (29.4) |
No Specific Country | FCNR(B) | 1,863 | (3.6) | 2,145 | (4.0) | 1,765 | (3.0) | 1,961 | (3.1) | 2,461 | (3.7) |
| | Borrowings | 902 | (1.5) | 921 | (1.5) | 22 | (—) | — | (—) | 382 | (0.6) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 17,682 | (18.6) | 12,498 | (12.7) | 12,131 | (12.1) | 13,732 | (13.0) | 12,736 | (11.8) |
| | Total | 22,414 | (7.8) | 17,566 | (6.2) | 25,485 | (8.3) | 18,477 | (5.8) | 19,173 | (5.7) |
Total | | FCNR(B) | 51,781 | (100.0) | 53,789 | (100.0) | 58,110 | (100.0) | 63,886 | (100.0) | 65,931 | (100.0) |
| | Borrowings | 59,323 | (100.0) | 60,021 | (100.0) | 63,722 | (100.0) | 70,407 | (100.0) | 66,533 | (100.0) |
| | NRE
Deposits | 95,033 | (100.0) | 98,461 | (100.0) | 1,00,310 | (100.0) | 1,05,982 | (100.0) | 1,07,846 | (100.0) |
| | Total | 2,88,871 | (100.0)
2,82,775 | (100.0) | 3,06,609 | (100.0) | 3,20,762 | (100.0) | 3,34,998 | (100.0) |
‘–’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total.
2. Totals
may not tally due to rounding off .
3. Data have been revised for previous
quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September
and December, respectively. |
Statement III: Country-wise
Breakup of Major Component of International Assets of Banks |
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(Rs. crore) |
Country | Major | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | | Components | | | | | | | | | | |
Australia | Export Bill | 456 | (1.7) | 392 | (1.4) | 571 | (1.8) | 808 | (2.3) | 155 | (0.4) |
| NOSTRO | 56 | (0.2) | 57 | (0.1) | 108 | (0.2) | 248 | (0.6) | 295 | (0.6) |
| Total | 537 | (0.4) | 512 | (0.3) | 835 | (0.5) | 1,121 | (0.7) | 551 | (0.3) |
Bahrain | Export Bill | 39 | (0.1) | 36 | (0.1) | 10 | (—) | 24 | (0.1) | 19 | (0.1) |
| NOSTRO | 1,890 | (5.8) | 1,673 | (4.1) | 1,098 | (2.5) | 1,756 | (4.5) | 2,822 | (6.0) |
| Total | 2,367 | (1.8) | 2,308 | (1.6) | 1,741 | (1.1) | 2,289 | (1.5) | 3,347 | (2.1) |
Belgium | Export Bill | 650 | (2.4) | 797 | (2.8) | 722 | (2.3) | 852 | (2.4) | 1,138 | (3.2) |
| NOSTRO | 28 | (0.1) | 29 | (0.1) | 63 | (0.1) | 490 | (1.3) | 465 | (1.0) |
| Total | 844 | (0.6) | 997 | (0.7) | 963 | (0.6) | 1,571 | (1.0) | 1,833 | (1.1) |
Canada | Export Bill | 249 | (0.9) | 252 | (0.9) | 285 | (0.9) | 395 | (1.1) | 393 | (1.1) |
| NOSTRO | 182 | (0.6) | 200 | (0.5) | 441 | (1.0) | 383 | (1.0) | 460 | (1.0) |
| Total | 747 | (0.6) | 872 | (0.6) | 1,288 | (0.8) | 1,385 | (0.9) | 1,431 | (0.9) |
China | Export Bill | 1,444 | (5.4) | 873 | (3.1) | 917 | (2.9) | 1,070 | (3.1) | 636 | (1.8) |
| NOSTRO | 6 | (—) | 1 | (—) | 98 | (0.2) | 2 | (—) | 2 | (—) |
| Total | 1,458 | (1.1) | 881 | (0.6) | 1,023 | (0.6) | 1,132 | (0.7) | 702 | (0.4) |
France | Export Bill | 445 | (1.7) | 467 | (1.7) | 838 | (2.7) | 900 | (9.0) | 586 | (1.6) |
| NOSTRO | 199 | (0.6) | 582 | (1.4) | 86 | (0.2) | 197 | (0.5) | 235 | (0.5) |
| Total | 880 | (0.7) | 1,291 | (0.9) | 1,224 | (0.8) | 1,425 | (0.9) | 1,156 | (0.7) |
Germany | Export Bill | 764 | (9.0) | 912 | (3.2) | 886 | (2.8) | 866 | (2.5) | 1,048 | (2.9) |
(Includes ECB) | NOSTRO | 1,065 | (3.3) | 3,073 | (7.5) | 2,031 | (4.6) | 1,671 | (4.3) | 2,028 | (4.3) |
| Total | 2,299 | (1.7) | 4,440 | (3.0) | 3,439 | (2.2) | 3,108 | (2.0) | 3,602 | (2.2) |
Hong Kong | Export Bill | 2,342 | (8.8) | 2,704 | (9.6) | 2,483 | (7.9) | 2,265 | (6.5) | 2,353 | (6.6) |
| NOSTRO | 752 | (2.3) | 1,334 | (3.2) | 1,488 | (3.3) | 1,263 | (3.2) | 1,414 | (3.0) |
| Total | 3,742 | (2.8) | 4,701 | (3.2) | 4,732 | (3.0) | 4,330 | (2.8) | 4,622 | (2.8) |
India | Export Bill | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) |
| NOSTRO | — | (—) | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | — | (—) | |
| Total | 61,703 | (45.6) | 61,761 | (42.1) | 63,566 | (40.2) | 62,779 | (40.7) | 61,751 | (37.9) |
Italy | Export Bill | 1,011 | (3.8) | 596 | (2.1) | 1,124 | (3.6) | 1,080 | (3.1) | 1,588 | (4.5) |
| NOSTRO | 43 | (0.1) | 117 | (0.3) | 155 | (0.3) | 194 | (0.5) | 413 | (0.9) |
| Total | 1,069 | (0.8) | 737 | (0.5) | 1,304 | (0.8) | 1,286 | (0.8) | 2,014 | (1.2) |
Japan | Export Bill | 451 | (1.7) | 399 | (1.4) | 190 | (0.6) | 665 | (1.9) | 247 | (0.7) |
| NOSTRO | 724 | (2.2) | 1,091 | (2.6) | 1,327 | (3.0) | 849 | (2.2) | 696 | (1.5) |
| Total | 1,578 | (1.2) | 1,892 | (1.3) | 1,967 | (1.2) | 2,023 | (1.3) | 1,471 | (0.9) |
Statement III:
Country-wise breakup of Major Components of International Assets of Banks |
(Based on LBS
Statements) (Concld.) | (Rs.
crore) | Country | Major
Components | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Netherlands
| Export Bill | 350 | (1.3) | 141 | (0.5) | 181 | (0.6) | 278 | (0.8) | 189 | (0.5) |
| | NOSTRO | 55 | (0.2) | 396 | (1.0) | 388 | (0.9) | 735 | (1.9) | 983 | (2.1) |
| | Total | 412 | (0.3) | 542 | (0.4) | 616 | (0.4) | 1,033 | (0.7) | 1,222 | (0.7) |
Singapore | Export
Bill | 1,032 | (3.9) | 1,412 | (5.0) | 996 | (3.2) | 1,384 | (4.0) | 1,231 | (3.5) |
| | NOSTRO | 1,194 | (3.7) | 1,347 | (3.3) | 1,708 | (3.8) | 2,125 | (5.5) | 3,759 | (8.0) |
| | Total | 3,480 | (2.6) | 4,081 | (2.8) | 4,167 | (2.6) | 5,080 | (3.3) | 6,675 | (4.1) |
Switzerland | Export
Bill | 150 | (0.6) | 109 | (0.4) | 208 | (0.7) | 856 | (2.4) | 830 | (2.3) |
(Includes BIS) | NOSTRO | 181 | (0.6) | 141 | (0.3) | 454 | (1.0) | 401 | (1.0) | 467 | (1.0) |
| | Total | 351 | (0.3) | 282 | (0.2) | 703 | (0.4) | 1,293 | (0.8) | 1,341 | (0.8) |
United Arab Emirates | Export
Bill | 2,146 | (8.1) | 2,467 | (8.8) | 2,001 | (6.3) | 1,575 | (4.5) | 2,136 | (6.0) |
| | NOSTRO | 40 | (0.1) | 145 | (0.4) | 64 | (0.1) | 127 | (0.3) | 216 | (0.5) |
| | Total | 3,450 | (2.6) | 3,915 | (2.7) | 3,316 | (2.1) | 3,094 | (2.0) | 3,732 | (2.3) |
United Kingdom | Export
Bill | 1,961 | (7.4) | 1,413 | (5.0) | 1,839 | (5.8) | 1,941 | (5.5) | 2,000 | (5.6) |
| | NOSTRO | 4,330 | (13.3) | 6,598 | (16.0) | 9,230 | (20.7) | 4,723 | (12.1) | 5,938 | (12.7) |
| | Total | 9,778 | (7.2) | 11,688 | (8.0) | 15,250 | (9.6) | 10,039 | (6.5) | 11,747 | (7.2) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
United States (Incl. | Export
Bill | 7,832 | (29.5) | 9,547 | (33.9) | 10,789 | (34.2) | 11,388 | (32.5) | 13,706 | (38.5) |
Midway Is., Wake | NOSTRO | 21,010 | (64.3) | 23,188 | (56.3) | 22,889 | (51.4) | 22,256 | (57.1) | 24,922 | (53.2) |
Islands) | Total | 31,421 | (23.2) | 35,770 | (24.4) | 37,140 | (23.5) | 37,423 | (24.3) | 42,585 | (26.1) |
No Specific Country | Export
Bill | 331 | (1.2) | 405 | (1.4) | 1,567 | (5.0) | 1,500 | (4.3) | 1,496 | (4.2) |
(Country unknown) | NOSTRO | 382 | (1.2) | 427 | (1.0) | 231 | (0.5) | 675 | (1.7) | 593 | (1.3) |
| | Total | 1,228 | (0.9) | 1,433 | (1.0) | 3,321 | (2.1) | 3,442 | (2.2) | 3,208 | (2.0) |
otal | | Export
Bill | 26,566 | (100.0) | 28,124 | (100.0) | 31,556 | (100.0) | 34,994 | (100.0) | 35,644 | (100.0) |
| | NOSTRO | 32,658 | (100.0) | 41,181 | (100.0) | 44,515 | (100.0) | 38,970 | (100.0) | 46,853 | (100.0) |
| | Total | 1,35,203 | (100.0)
1,46,537 | (100.0) | 1,58,201 | (100.0) | 1,54,204 | (100.0) | 1,62,991 | (100.0) |
‘–’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total.
2. Totals
may not tally due to rounding off .
3. Data have been revised for previous
quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September
and December, respectively. |
Statement IV: Currency and
Sector-wise Breakup of International Liabilities/Assets of Banks |
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(Rs. crore) |
Currency | International
Liabilities | | | All
Sector | Non-Bank Sector |
| | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Q3: 2005 | Q4:
2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | Swiss
Franc | 105 | 88 | 176 | 171 | 140 | 22 | 21 | 79 | 126 | 121 |
| | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) |
Euro | | 5,291 | 4,861 | 5,780 | 5,746 | 6,090 | 3,336 | 3,108 | 4,093 | 3,813 | 4,113 |
| | (1.8) | (1.7) | (1.9) | (1.8) | (1.8) | (1.6) | (1.5) | (1.8) | (1.6) | (1.6) |
Pound Sterling | 15,081 | 15,436 | 16,734 | 18,584 | 23,057 | 14,164 | 14,413 | 16,086 | 18,039 | 22,070 |
| | (5.2) | (5.5) | (5.5) | (5.8) | (6.9) | (6.9) | (6.9) | (7.1) | (7.7) | (8.8) |
Indian Rupee | 122,828 | 135,938 | 152,018 | 153,754 | 165,500 | 114,814 | 124,495 | 139,328 | 140,964 | 152,524 |
| | (42.5) | (48.1) | (49.6) | (47.9) | (49.4) | (56.0) | (59.8) | (61.6) | (60.5) | (60.8) |
Japanese Yen | 7,294 | 8,208 | 8,836 | 8,364 | 8,405 | 989 | 1,202 | 865 | 1,031 | 828 |
| | (2.5) | (2.9) | (2.9) | (2.6) | (2.5) | (0.5) | (0.6) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.3) |
Other Foreign | 1,556 | 1,172 | 825 | 1,242 | 1,193 | 46 | 99 | 90 | 381 | 449 |
Currencies | (0.5) | (0.4) | (0.3) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.2) | (0.2) |
US Dollar | 136,715 | 117,071 | 122,240 | 132,900 | 130,611 | 71,513 | 65,016 | 65,466 | 68,682 | 70,616 |
| | (47.3) | (41.4) | (39.9) | (41.4) | (39.0) | (34.9) | (31.2) | (29.0) | (29.5) | (28.2) |
Total Intl. | 288,871 | 282,775 | 306,609 | 320,762 | 334,998 | 204,885 | 208,354 | 226,008 | 233,035 | 250,723 |
Liabilities | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
International Assets |
Swiss Franc | 208 | 166 | 324 | 461 | 699 | 18 | 25 | 47 | 60 | 219 |
| | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.4) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.2) |
Euro | | 5,536 | 5,073 | 6,009 | 7,643 | 8,008 | 3,352 | 2,889 | 3,621 | 4,645 | 4,228 |
| | (4.1) | (3.5) | (3.8) | (5.0) | (4.9) | (4.1) | (3.4) | (3.9) | (4.8) | (4.4) |
Pound Sterling | 6,448 | 5,620 | 5,903 | 5,519 | 5,782 | 1,110 | 940 | 1,504 | 1,284 | 1,682 |
| | (4.8) | (3.8) | (3.7) | (3.6) | (3.5) | (1.4) | (1.1) | (1.6) | (1.3) | (1.8) |
Indian Rupee | 4,390 | 5,381 | 7,135 | 6,747 | 7,420 | 4,370 | 5,313 | 7,081 | 6,693 | 7,365 |
| | (3.2) | (3.7) | (4.5) | (4.4) | (4.6) | (5.3) | (6.2) | (7.6) | (7.0) | (7.7) |
Japanese Yen | 2,212 | 2,867 | 3,467 | 3,034 | 2,819 | 1,285 | 1,270 | 1,956 | 1,665 | 1,415 |
| | (1.6) | (2.0) | (2.2) | (2.0) | (1.7) | (1.6) | (1.5) | (2.1) | (1.7) | (1.5) |
Other Foreign | 4,618 | 4,573 | 5,347 | 5,877 | 6,953 | 970 | 557 | 1,022 | 813 | 789 |
Currencies | (3.4) | (3.1) | (3.4) | (3.8) | (4.3) | (1.2) | (0.7) | (1.1) | (0.8) | (0.8) |
US Dollar | 111,791 | 122,858 | 130,016 | 124,923 | 131,309 | 71,043 | 74,504 | 77,484 | 80,806 | 79,962 |
| | (82.7) | (83.8) | (82.2) | (81.0) | (80.6) | (86.5) | (87.1) | (83.6) | (84.2) | (83.6) |
Total Intl. Assets | 135,203 | 146,537 | 158,201 | 154,204 | 162,991 | 82,147 | 85,498 | 92,715 | 95,967 | 95,661 |
| | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
‘–’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes : 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective
group (column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
3. Data have
been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended
March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement V: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Country of Residence of |
Transacting Units (Based
on LBS Statements) - Amount Outstanding as at end | (Rs.
crore) | Country | International
Liabilities | | All
Currencies | Foreign Currencies |
| Q3: 2005 | Q4:
2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Total Intl. | 288,871 | 282,775 | 306,609 | 320,762 | 334,998 | 166,043 | 146,836 | 154,591 | 167,007 | 169,497 |
Liabilities | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
of which: | | | | | | | | | | |
Bahrain | 4,462 | 4,842 | 4,432 | 5,588 | 4,945 | 2,970 | 3,116 | 2,639 | 3,094 | 2,733 |
| (1.5) | (1.7) | (1.4) | (1.7) | (1.5) | (1.8) | (2.1) | (1.7) | (1.9) | (1.6) |
Canada | 3,258 | 3,272 | 3,181 | 3,550 | 4,044 | 1,474 | 1,386 | 1,293 | 1,595 | 1,628 |
| (1.1) | (1.2) | (1.0) | (1.1) | (1.2) | (0.9) | (0.9) | (0.8) | (1.0) | (1.0) |
Germany | 6,901 | 7,251 | 6,933 | 7,408 | 7,725 | 5,326 | 5,029 | 4,930 | 5,478 | 5,738 |
(Includes ECB) | (2.4) | (2.6) | (2.3) | (2.3) | (2.3) | (3.2) | (3.4) | (3.2) | (3.3) | (3.4) |
Hong Kong | 10,933 | 8,808 | 8,131 | 8,930 | 9,567 | 7,883 | 5,552 | 5,028 | 6,010 | 6,098 |
| (3.8) | (3.1) | (2.7) | (2.8) | (2.9) | (4.7) | (3.8) | (3.3) | (3.6) | (3.6) |
India | 16,795 | 14,202 | 12,518 | 14,974 | 14,925 | 16,795 | 14,202 | 12,518 | 14,974 | 14,925 |
| (5.8) | (5.0) | (4.1) | (4.7) | (4.5) | (10.1) | (9.7) | (8.1) | (9.0) | (8.8) |
Kuwait | 6,183 | 6,651 | 7,011 | 6,113 | 6,108 | 1,851 | 1,605 | 1,713 | 1,935 | 2,003 |
| (2.1) | (2.4) | (2.3) | (1.9) | (1.8) | (1.1) | (1.1) | (1.1) | (1.2) | (1.2) |
Mauritius | 5,996 | 9,645 | 12,676 | 11,826 | 17,869 | 1,459 | 172 | 193 | 125 | 273 |
| (2.1) | (3.4) | (4.1) | (3.7) | (5.3) | (0.9) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.2) |
Netherlands | 5,681 | 4,985 | 5,836 | 6,956 | 6,224 | 3,642 | 2,742 | 3,209 | 4,208 | 3,258 |
| (2.0) | (1.8) | (1.9) | (2.2) | (1.9) | (2.2) | (1.9) | (2.1) | (2.5) | (1.9) |
Oman | 5,184 | 4,050 | 4,851 | 5,463 | 4,151 | 1,430 | 822 | 1,812 | 1,963 | 1,076 |
| (1.8) | (1.4) | (1.6) | (1.7) | (1.2) | (0.9) | (0.6) | (1.2) | (1.2) | (0.6) |
Saudi Arabia | 8,572 | 8,620 | 9,487 | 9,772 | 9,156 | 2,277 | 1,733 | 1,501 | 2,331 | 1,650 |
| (3.0) | (3.0) | (3.1) | (3.0) | (2.7) | (1.4) | (1.2) | (1.0) | (1.4) | (1.0) |
Singapore | 15,685 | 14,843 | 15,658 | 15,706 | 13,984 | 10,567 | 11,099 | 11,441 | 11,945 | 9,420 |
| (5.4) | (5.2) | (5.1) | (4.9) | (4.2) | (6.4) | (7.6) | (7.4) | (7.2) | (5.6) |
United Arab | 27,342 | 22,881 | 25,018 | 29,495 | 27,364 | 12,327 | 5,208 | 7,406 | 8,786 | 8,626 |
Emirates | (9.5) | (8.1) | (8.2) | (9.2) | (8.2) | (7.4) | (3.5) | (4.8) | (5.3) | (5.1) |
United Kingdom @ | 37,333 | 35,871 | 40,961 | 41,507 | 52,066 | 25,887 | 23,531 | 25,420 | 25,920 | 32,318 |
| (12.9) | (12.7) | (13.4) | (12.9) | (15.5) | (15.6) | (16.0) | (16.4) | (15.5) | (19.1) |
United States # | 74,411 | 82,110 | 84,301 | 98,971 | 98,561 | 48,114 | 49,326 | 50,375 | 58,397 | 58,592 |
| (25.8) | (29.0) | (27.5) | (30.9) | (29.4) | (29.0) | (33.6) | (32.6) | (35.0) | (34.6) |
No Specific | 22,414 | 17,566 | 25,485 | 18,477 | 19,173 | 3,199 | 3,726 | 5,758 | 2,101 | 2,971 |
Country | (7.8) | (6.2) | (8.3) | (5.8) | (5.7) | (1.9) | (2.5) | (3.7) | (1.3) | (1.8) |
Statement V: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Country of |
Residence of Transacting Units
(Based on LBS Statements) - Amount Outstanding as at end | (Rs.
crore) | Country | | International
Assets | | | All
Currencies | Foreign Currencies |
| | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Q3: 2005 | Q4:
2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 |
Total Intl. Assets | 135,203 | 146,537 | 158,201 | 154,204 | 162,991 | 130,813 | 141,157 | 151,066 | 147,457 | 155,571 |
of which: | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
Bahrain | | 2,367 | 2,308 | 1,741 | 2,289 | 3,347 | 2,326 | 2,251 | 1,677 | 2,210 | 3,282 |
| | (1.8) | (1.6) | (1.1) | (1.5) | (2.1) | (1.8) | (1.6) | (1.1) | (1.5) | (2.1) |
Belgium | | 844 | 997 | 963 | 1,571 | 1,833 | 828 | 981 | 951 | 1,550 | 1,811 |
| | (0.6) | (0.7) | (0.6) | (1.0) | (1.1) | (0.6) | (0.7) | (0.6) | (1.1) | (1.2) |
Canada | | 747 | 872 | 1,288 | 1,385 | 1,431 | 714 | 827 | 1,240 | 1,337 | 1,386 |
| | (0.6) | (0.6) | (0.8) | (0.9) | (0.9) | (0.5) | (0.6) | (0.8) | (0.9) | (0.9) |
Germany | | 2,299 | 4,440 | 3,439 | 3,108 | 3,602 | 2,252 | 4,386 | 3,361 | 3,031 | 3,556 |
(Includes ECB) | (1.7) | (3.0) | (2.2) | (2.0) | (2.2) | (1.7) | (3.1) | (2.2) | (2.1) | (2.3) |
Hong Kong | 3,742 | 4,701 | 4,732 | 4,330 | 4,622 | 3,682 | 4,660 | 4,679 | 4,300 | 4,560 |
| | (2.8) | (3.2) | (3.0) | (2.8) | (2.8) | (2.8) | (3.3) | (3.1) | (2.9) | (2.9) |
India | | 61,703 | 61,761 | 63,566 | 62,779 | 61,751 | 61,703 | 61,761 | 63,566 | 62,779 | 61,751 |
| | (45.6) | (42.1) | (40.2) | (40.7) | (37.9) | (47.2) | (43.8) | (42.1) | (42.6) | (39.7) |
Italy | | 1,069 | 737 | 1,304 | 1,286 | 2,014 | 1,058 | 723 | 1,284 | 1,274 | 1,995 |
| | (0.8) | (0.5) | (0.8) | (0.8) | (1.2) | (0.8) | (0.5) | (0.8) | (0.9) | (1.3) |
Japan | | 1,578 | 1,892 | 1,967 | 2,023 | 1,471 | 1,561 | 1,875 | 1,948 | 1,989 | 1,447 |
| | (1.2) | (1.3) | (1.2) | (1.3) | (0.9) | (1.2) | (1.3) | (1.3) | (1.3) | (0.9) |
Netherlands | 412 | 542 | 616 | 1,033 | 1,222 | 407 | 536 | 608 | 1,025 | 1,211 |
| | (0.3) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.7) | (0.7) | (0.3) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.7) | (0.8) |
Singapore | 3,480 | 4,081 | 4,167 | 5,080 | 6,675 | 3,379 | 3,932 | 3,942 | 4,843 | 6,319 |
| | (2.6) | (2.8) | (2.6) | (3.3) | (4.1) | (2.6) | (2.8) | (2.6) | (3.3) | (4.1) |
Switzerland | 351 | 282 | 703 | 1,293 | 1,341 | 335 | 253 | 664 | 1,259 | 1,126 |
(Includes BIS) | (0.3) | (0.2) | (0.4) | (0.8) | (0.8) | (0.3) | (0.2) | (0.4) | (0.9) | (0.7) |
United Arab | 3,450 | 3,915 | 3,316 | 3,094 | 3,732 | 3,041 | 3,481 | 2,752 | 2,491 | 2,996 |
Emirates | | (2.6) | (2.7) | (2.1) | (2.0) | (2.3) | (2.3) | (2.5) | (1.8) | (1.7) | (1.9) |
United Kingdom @ | 9,778 | 11,688 | 15,250 | 10,039 | 11,747 | 9,475 | 11,271 | 14,894 | 9,677 | 11,342 |
| | (7.2) | (8.0) | (9.6) | (6.5) | (7.2) | (7.2) | (8.0) | (9.9) | (6.6) | (7.3) |
United States # | 31,421 | 35,770 | 37,140 | 37,423 | 42,585 | 29,200 | 33,228 | 33,955 | 34,243 | 38,874 |
| | (23.2) | (24.4) | (23.5) | (24.3) | (26.1) | (22.3) | (23.5) | (22.5) | (23.2) | (25.0) |
No Specific | 1,228 | 1,433 | 3,321 | 3,442 | 3,208 | 954 | 974 | 2,060 | 2,371 | 2,391 |
Country | | (0.9) | (1.0) | (2.1) | (2.2) | (2.0) | (0.7) | (0.7) | (1.4) | (1.6) | (1.5) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
@ : Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and
Jersey. #: Includes Miday Island and Wake Islands.
‘-’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes :
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective
group (column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off .
3. “No
Specific Country” means the country information has not been provided by
the reporting bank branches.
4. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
5. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December,
respectively. |
Statement VI: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Country of Incorpora- |
tion of Banks (Based on LBS
Statements) - Amount Outstanding as at end | (Rs.
crore) | Country of | International
Liabilities | Incorporation of Bank | Total:
All Sectors | Position vis-à-vis
Banks | | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Q3: 2005 | Q4:
2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | Bahrain
| 310 | 307 | 315 | 320 | 327 | 73 | 72 | 59 | 62 | 59 |
| (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Bangladesh | 39 | 35 | 43 | 51 | 49 | 39 | 34 | 43 | 50 | 48 |
| (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Belgium | 686 | 647 | 603 | 626 | 588 | 646 | 602 | 561 | 584 | 546 |
| (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.8) | (0.8) | (0.7) | (0.7) | (0.6) |
Canada | 2,182 | 1,893 | 1,272 | 1,811 | 2,124 | 2,078 | 1,785 | 1,177 | 1,701 | 1,997 |
| (0.8) | (0.7) | (0.4) | (0.6) | (0.6) | (2.5) | (2.4) | (1.5) | (1.9) | (2.4) |
France | 2,412 | 3,119 | 2,966 | 2,991 | 3,342 | 1,563 | 2,065 | 1,876 | 1,901 | 2,499 |
| (0.8) | (1.1) | (1.0) | (0.9) | (1.0) | (1.9) | (2.8) | (2.3) | (2.2) | (3.0) |
Germany | 3,168 | 2,901 | 3,497 | 3,847 | 4,108 | 1,481 | 1,444 | 1,679 | 1,894 | 1,556 |
| (1.1) | (1.0) | (1.1) | (1.2) | (1.2) | (1.8) | (1.9) | (2.1) | (2.2) | (1.8) |
Hong Kong | 11,223 | 13,040 | 14,365 | 15,293 | 14,971 | 3,220 | 3,132 | 3,308 | 2,727 | 3,750 |
| (3.9) | (4.6) | (4.7) | (4.8) | (4.5) | (3.8) | (4.2) | (4.1) | (3.1) | (4.4) |
India | 238,366 | 229,326 | 245,682 | 255,672 | 270,325 | 59,364 | 48,946 | 50,897 | 56,443 | 53,385 |
| (82.5) | (81.1) | (80.1) | (79.7) | (80.7) | (70.7) | (65.8) | (63.1) | (64.3) | (63.3) |
Indonesia | 102 | 98 | 102 | 95 | 104 | 100 | 96 | 100 | 93 | 102 |
| (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Japan | 728 | 380 | 559 | 887 | 900 | 624 | 344 | 523 | 660 | 777 |
| (0.3) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.3) | (0.7) | (0.5) | (0.6) | (0.8) | (0.9) |
Mauritius | 153 | 154 | 145 | 142 | 142 | 127 | 127 | 125 | 123 | 120 |
| (0.1) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Netherlands | 5,787 | 5,398 | 6,466 | 7,388 | 6,793 | 3,087 | 4,537 | 5,451 | 6,322 | 5,628 |
| (2.0) | (1.9) | (2.1) | (2.3) | (2.0) | (3.7) | (6.1) | (6.8) | (7.2) | (6.7) |
Oman | 266 | 256 | 251 | 248 | 219 | 54 | 47 | 40 | 48 | 23 |
| (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) |
Singapore | 1,061 | 1,188 | 1,374 | 1,627 | 1,702 | 1,057 | 1,184 | 1,370 | 1,621 | 1,686 |
| (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.5) | (0.5) | (1.3) | (1.6) | (1.7) | (1.8) | (2.0) |
South Korea | 78 | 87 | 147 | 80 | 71 | 75 | 87 | 94 | 71 | 68 |
| (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Sri Lanka | 92 | 94 | 96 | 99 | 102 | 49 | 50 | 53 | 59 | 59 |
| (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Taiwan, China | 456 | 377 | 325 | 280 | 252 | 455 | 377 | 325 | 280 | 252 |
| (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.5) | (0.5) | (0.4) | (0.3) | (0.3) |
Thailand | 40 | 42 | 41 | 43 | 75 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
United Arab Emirates | 542 | 533 | 484 | 581 | 542 | 134 | 182 | 98 | 134 | 118 |
| (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.1) |
United Kingdom | 8,573 | 8,820 | 11,980 | 11,880 | 11,492 | 4,046 | 3,661 | 6,096 | 5,893 | 5,383 |
| (3.0) | (3.1) | (3.9) | (3.7) | (3.4) | (4.8) | (4.9) | (7.6) | (6.7) | (6.4) |
United States | 12,610 | 14,080 | 15,895 | 16,803 | 16,770 | 5,678 | 5,615 | 6,688 | 7,027 | 6,183 |
| (4.4) | (5.0) | (5.2) | (5.2) | (5.0) | (6.8) | (7.5) | (8.3) | (8.0) | (7.3) |
Total Intl. Liabilities | 288,871 | 282,775 | 306,609 | 320,762 | 334,998 | 83,987 | 74,421 | 80,600 | 87,726 | 84,275 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
Statement VI: International
Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified according to Country of |
Incorporation of Banks (Based
on LBS Statements) - Amount Outstanding as at end (Concld.) |
(Rs. crore) |
Country of | International
Assets | Incorporation | Total:
All Sectors | Position vis-à-vis
Banks | of Bank | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Q3:
2005 | Q4: 2005 | Q1:
2006 | Q2: 2006 | Q3:
2006 | Q3: 2005 | Q4:
2005 | Q1: 2006 | Q2:
2006 | Q3: 2006 | Bahrain
| | 85 | 85 | 96 | 58 | 54 | 1 | 23 | 40 | 12 | 18 |
| | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) |
Bangladesh | 8 | 7 | 13 | 20 | 14 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 16 | 9 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Belgium | | 433 | 409 | 362 | 381 | 379 | 61 | 107 | 65 | 39 | 52 |
| | (0.3) | (0.3) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
Canada | | 1,359 | 1,268 | 1,119 | 1,073 | 961 | 24 | 18 | 14 | 32 | 48 |
| | (1.0) | (0.9) | (0.7) | (0.7) | (0.6) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.1) |
France | | 334 | 782 | 870 | 1,044 | 879 | 30 | 476 | 605 | 756 | 666 |
| | (0.2) | (0.5) | (0.5) | (0.7) | (0.5) | (0.1) | (0.8) | (0.9) | (1.3) | (1.0) |
Germany | | 3,582 | 3,407 | 3,894 | 4,266 | 4,406 | 3,445 | 2,952 | 3,262 | 3,681 | 3,578 |
| | (2.6) | (2.3) | (2.5) | (2.8) | (2.7) | (6.5) | (4.8) | (5.0) | (6.3) | (5.3) |
Hong Kong | 2,572 | 3,983 | 4,948 | 3,098 | 3,551 | 401 | 1,626 | 2,230 | 542 | 200 |
| | (1.9) | (2.7) | (3.1) | (2.0) | (2.2) | (0.8) | (2.7) | (3.4) | (0.9) | (0.3) |
India | | 110,886 | 119,281 | 122,438 | 124,497 | 132,535 | 46,356 | 51,301 | 51,235 | 49,662 | 56,878 |
| | (82.0) | (81.4) | (77.4) | (80.7) | (81.3) | (87.4) | (84.0) | (78.2) | (85.3) | (84.5) |
Indonesia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Japan | | 46 | 41 | 231 | 236 | 207 | 46 | 41 | 103 | 197 | 158 |
| | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.2) |
Mauritius | 50 | 23 | 41 | 28 | 10 | 29 | 2 | 22 | 11 | 6 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Netherlands | 4,768 | 4,847 | 5,667 | 5,707 | 3,937 | 57 | 93 | 260 | 340 | 115 |
| | (3.5) | (3.3) | (3.6) | (3.7) | (2.4) | (0.1) | (0.2) | (0.4) | (0.6) | (0.2) |
Oman | | 10 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 8 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Singapore | 174 | 195 | 779 | 1,249 | 1,453 | 41 | 45 | 608 | 812 | 1,013 |
| | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.5) | (0.8) | (0.9) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.9) | (1.4) | (1.5) |
South Korea | 23 | 14 | 91 | 28 | 20 | 11 | 0 | 69 | 19 | 13 |
| | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) |
Sri Lanka | | 16 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Taiwan, China | 5 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
Thailand | | 4 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
| | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
United Arab Emirates | 95 | 85 | 68 | 86 | 77 | 37 | 14 | 13 | 15 | 24 |
| | (0.1) | (0.1) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (0.1) | (—) | (—) | (—) | (—) |
United Kingdom | 2,790 | 3,973 | 7,968 | 4,871 | 4,786 | 144 | 1,070 | 3,423 | 721 | 717 |
| | (2.1) | (2.7) | (5.0) | (3.2) | (2.9) | (0.3) | (1.8) | (5.2) | (1.2) | (1.1) |
United States | 7,961 | 8,107 | 9,592 | 7,539 | 9,694 | 2,348 | 3,251 | 3,513 | 1,366 | 3,814 |
| | (5.9) | (5.5) | (6.1) | (4.9) | (5.9) | (4.4) | (5.3) | (5.4) | (2.3) | (5.7) |
Total Intl. Asset | 135,203 | 146,537 | 158,201 | 154,204 | 162,991 | 53,056 | 61,039 | 65,485 | 58,237 | 67,330 |
| | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
‘-’ : Nil/Negligible.
Notes
:
1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective
group (Column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
3. Data have
been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended
March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement VII: Residual Maturity
and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International |
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements)
- Amount Outstanding as at | end
of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis | (Rs.
crore) | Country
of Transacting Units | Period | Total
| Residual Maturity | Sector |
| | International
Claims | Short Term | Long
Term | Un- allocated | Bank | Non-Bank
Public | Non-Bank Private |
Total Intl. Claims | Sep-2005 | 66,919 | 53,028 | 12,899 | 993 | 25,251 | 1,396 | 40,273 |
| Dec-2005 | 88,085 | 70,362 | 16,605 | 1,118 | 40,896 | 1,446 | 45,744 |
| Mar-2006 | 92,711 | 73,176 | 18,627 | 907 | 43,050 | 1,248 | 48,413 |
| Jun-2006 | 99,317 | 74,013 | 24,227 | 1,078 | 40,580 | 732 | 58,005 |
| Sep-2006 | 114,688 | 86,175 | 27,796 | 716 | 49,932 | 840 | 63,916 |
Australia | Sep-2005 | 599 | 516 | 51 | 32 | 100 | 1 | 499 |
| Dec-2005 | 671 | 445 | 226 | — | 141 | — | 530 |
| Mar-2006 | 805 | 694 | 111 | — | 137 | — | 668 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,532 | 1,088 | 444 | — | 638 | — | 893 |
| Sep-2006 | 1,132 | 425 | 707 | — | 849 | 1 | 282 |
Austria | Sep-2005 | 73 | 45 | 28 | — | 61 | — | 13 |
| Dec-2005 | 907 | 776 | 131 | — | 836 | — | 71 |
| Mar-2006 | 874 | 795 | 79 | — | 764 | — | 109 |
| Jun-2006 | 645 | 610 | 35 | — | 548 | — | 97 |
| Sep-2006 | 521 | 431 | 90 | — | 413 | — | 108 |
Bahamas | Sep-2005 | 1,303 | 1,303 | — | — | 1,047 | — | 256 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,079 | 1,079 | — | — | 1,055 | — | 24 |
| Mar-2006 | 777 | 777 | — | — | 770 | — | 7 |
| Jun-2006 | 552 | 506 | 46 | — | 506 | — | 46 |
| Sep-2006 | 900 | 426 | 474 | — | 138 | — | 762 |
Bahrain | Sep-2005 | 1,628 | 1,183 | 445 | — | 1,547 | — | 81 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,806 | 579 | 1,228 | — | 1,703 | — | 103 |
| Mar-2006 | 2,194 | 980 | 1,213 | — | 2,024 | — | 170 |
| Jun-2006 | 2,606 | 1,359 | 1,247 | — | 2,121 | — | 485 |
| Sep-2006 | 2,173 | 970 | 1,203 | — | 1,830 | 5 | 338 |
Belgium | Sep-2005 | 1,053 | 960 | 93 | — | 163 | — | 890 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,479 | 1,401 | 78 | — | 127 | — | 1,353 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,479 | 1,395 | 83 | — | 414 | — | 1,065 |
| Jun-2006 | 2,942 | 2,820 | 121 | — | 1,474 | — | 1,468 |
| Sep-2006 | 2,826 | 2,517 | 309 | — | 583 | — | 2,243 |
Canada | Sep-2005 | 548 | 476 | 71 | — | 121 | 4 | 422 |
| Dec-2005 | 624 | 543 | 81 | — | 214 | 1 | 409 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,181 | 973 | 208 | — | 556 | 2 | 622 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,219 | 1,030 | 189 | — | 688 | 3 | 528 |
| Sep-2006 | 1,615 | 1,380 | 235 | — | 1,063 | 2 | 550 |
China | Sep-2005 | 1,423 | 1,422 | 2 | — | 6 | — | 1,417 |
| Dec-2005 | 853 | 845 | 8 | — | 1 | — | 852 |
| Mar-2006 | 977 | 971 | 5 | 1 | 98 | — | 879 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,025 | 1,013 | 12 | 1 | 2 | — | 1,023 |
| Sep-2006 | 561 | 526 | 34 | 1 | 2 | — | 559 |
Cyprus | Sep-2005 | 89 | 61 | 28 | — | 27 | — | 63 |
| Dec-2005 | 107 | 79 | 29 | — | 27 | — | 81 |
| Mar-2006 | 94 | 92 | 3 | — | — | — | 94 |
| Jun-2006 | 220 | 102 | 118 | — | 115 | — | 104 |
| Sep-2006 | 887 | 801 | 86 | — | 84 | — | 802 |
Statement VII: Residual Maturity
and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International |
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements)
- Amount Outstanding as at | end
of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Contd.) |
(Rs. crore) | Country
of Transacting | Period | Total | Residual
Maturity | Sector |
Units | | International | Short | Long | Un- | Bank | Non-Bank | Non-Bank |
| | Claims | Term | Term | allocated | | Public | Private |
Denmark | Sep-2005 | 132 | 112 | 20 | — | 57 | — | 75 |
| Dec-2005 | 296 | 275 | 21 | — | 228 | — | 68 |
| Mar-2006 | 841 | 819 | 22 | — | 689 | — | 152 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,044 | 984 | 60 | — | 954 | — | 90 |
| Sep-2006 | 687 | 450 | 237 | — | 544 | — | 143 |
France | Sep-2005 | 1,046 | 912 | 134 | — | 468 | — | 578 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,789 | 1,641 | 148 | — | 689 | — | 1,099 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,460 | 1,106 | 354 | — | 548 | — | 912 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,874 | 1,478 | 396 | — | 743 | — | 1,130 |
| Sep-2006 | 1,745 | 1,258 | 487 | — | 752 | — | 993 |
Germany (includes ECB) | Sep-2005 | 1,867 | 1,670 | 166 | 31 | 888 | 58 | 921 |
| Dec-2005 | 5,233 | 4,942 | 248 | 42 | 4,154 | 48 | 1,030 |
| Mar-2006 | 4,678 | 4,226 | 451 | — | 3,600 | 60 | 1,018 |
| Jun-2006 | 5,108 | 4,738 | 369 | — | 3,823 | 66 | 1,218 |
| Sep-2006 | 5,035 | 4,169 | 866 | — | 3,788 | 55 | 1,192 |
Hong Kong | Sep-2005 | 5,125 | 3,120 | 2,005 | — | 1,557 | 25 | 3,544 |
| Dec-2005 | 6,221 | 5,501 | 721 | — | 2,324 | — | 3,897 |
| Mar-2006 | 6,652 | 6,183 | 469 | — | 3,315 | — | 3,337 |
| Jun-2006 | 4,999 | 4,250 | 749 | — | 2,101 | — | 2,898 |
| Sep-2006 | 4,944 | 3,919 | 1,025 | — | 2,095 | 1 | 2,848 |
Indonesia | Sep-2005 | 697 | 619 | 78 | — | 36 | — | 661 |
| Dec-2005 | 791 | 731 | 60 | — | 1 | — | 790 |
| Mar-2006 | 955 | 796 | 136 | 23 | 0 | 45 | 910 |
| Jun-2006 | 964 | 834 | 130 | — | 8 | — | 956 |
| Sep-2006 | 1,071 | 837 | 234 | — | 469 | — | 602 |
Ireland | Sep-2005 | 220 | 216 | 4 | — | 141 | — | 79 |
| Dec-2005 | 404 | 352 | 51 | — | 259 | — | 144 |
| Mar-2006 | 437 | 429 | 8 | — | 385 | — | 52 |
| Jun-2006 | 483 | 477 | 5 | — | 378 | — | 104 |
| Sep-2006 | 761 | 634 | 127 | — | 473 | — | 288 |
Italy | Sep-2005 | 1,071 | 1,053 | 18 | — | 76 | — | 995 |
| Dec-2005 | 823 | 720 | 103 | — | 245 | — | 578 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,266 | 1,260 | 6 | — | 156 | — | 1,109 |
| Jun-2006 | 2,264 | 1,670 | 594 | — | 1,140 | — | 1,124 |
| Sep-2006 | 2,801 | 2,270 | 530 | — | 1,221 | — | 1,579 |
Japan | Sep-2005 | 1,318 | 1,151 | 166 | — | 623 | 1 | 693 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,327 | 1,259 | 66 | 2 | 765 | — | 562 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,007 | 904 | 103 | — | 713 | — | 294 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,833 | 1,648 | 183 | 1 | 941 | 1 | 891 |
| Sep-2006 | 2,451 | 2,090 | 361 | — | 1,391 | — | 1,060 |
Kuwait | Sep-2005 | 333 | 176 | 157 | — | 59 | — | 275 |
| Dec-2005 | 658 | 337 | 321 | — | 58 | — | 600 |
| Mar-2006 | 285 | 69 | 216 | — | 52 | — | 232 |
| Jun-2006 | 315 | 84 | 231 | — | 85 | — | 231 |
| Sep-2006 | 530 | 316 | 213 | — | 73 | — | 457 |
Statement VII: Residual Maturity
and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International |
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements)
- Amount Outstanding as at | end
of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Contd.) |
(Rs. crore) | Country
of Transacting | Period | Total | Residual
Maturity | Sector |
Units | | International | Short | Long | Un- | Bank | Non-Bank | Non-Bank |
| | Claims | Term | Term | allocated | | Public | Private |
Luxembourg | Sep-2005 | 6 | 6 | 1 | — | — | — | 6 |
| Dec-2005 | 589 | 6 | 583 | — | 257 | — | 332 |
| Mar-2006 | 465 | 5 | 459 | — | 104 | — | 361 |
| Jun-2006 | 467 | 11 | 456 | — | 59 | — | 408 |
| Sep-2006 | 514 | 211 | 303 | — | 48 | — | 466 |
Netherlands | Sep-2005 | 1,139 | 800 | 339 | — | 582 | — | 557 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,243 | 648 | 397 | 198 | 951 | — | 291 |
| Mar-2006 | 1,092 | 758 | 154 | 180 | 717 | — | 375 |
| Jun-2006 | 3,758 | 2,698 | 1,059 | — | 1,366 | — | 2,391 |
| Sep-2006 | 4,528 | 3,808 | 720 | — | 2,271 | — | 2,257 |
Russia | Sep-2005 | 802 | 432 | 370 | — | 387 | — | 416 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,331 | 817 | 514 | — | 542 | — | 789 |
| Mar-2006 | 2,134 | 778 | 1,291 | 66 | 1,078 | — | 1,056 |
| Jun-2006 | 3,005 | 1,572 | 1,433 | — | 1,677 | — | 1,328 |
| Sep-2006 | 3,765 | 2,749 | 1,016 | — | 2,220 | — | 1,545 |
Saudi Arabia | Sep-2005 | 429 | 288 | 141 | — | 4 | — | 425 |
| Dec-2005 | 550 | 369 | 181 | — | 8 | — | 541 |
| Mar-2006 | 677 | 335 | 341 | — | 211 | — | 466 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,059 | 548 | 511 | — | 276 | — | 783 |
| Sep-2006 | 768 | 251 | 517 | — | 260 | — | 508 |
Singapore | Sep-2005 | 2,815 | 2,614 | 201 | — | 561 | 8 | 2,246 |
| Dec-2005 | 3,495 | 3,082 | 396 | 17 | 661 | 8 | 2,826 |
| Mar-2006 | 4,182 | 3,527 | 652 | 3 | 1,412 | 9 | 2,761 |
| Jun-2006 | 5,673 | 4,981 | 669 | 23 | 1,876 | — | 3,797 |
| Sep-2006 | 7,066 | 5,759 | 1,282 | 25 | 2,618 | — | 4,448 |
South Korea | Sep-2005 | 351 | 267 | 84 | — | 208 | 13 | 131 |
| Dec-2005 | 367 | 170 | 162 | 35 | 194 | — | 173 |
| Mar-2006 | 149 | 103 | 45 | — | 40 | — | 109 |
| Jun-2006 | 364 | 174 | 190 | — | 240 | — | 124 |
| Sep-2006 | 909 | 589 | 321 | — | 749 | — | 160 |
Spain | Sep-2005 | 485 | 399 | 85 | — | 33 | — | 452 |
| Dec-2005 | 384 | 362 | 22 | — | 71 | — | 313 |
| Mar-2006 | 806 | 782 | 24 | — | 304 | — | 502 |
| Jun-2006 | 902 | 876 | 25 | — | 192 | — | 710 |
| Sep-2006 | 766 | 733 | 33 | — | 202 | — | 564 |
Sri Lanka | Sep-2005 | 843 | 746 | 97 | — | 27 | 53 | 764 |
| Dec-2005 | 1,204 | 1,042 | 162 | — | 231 | 38 | 934 |
| Mar-2006 | 862 | 698 | 165 | — | 167 | 38 | 657 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,534 | 1,378 | 156 | — | 291 | — | 1,243 |
| Sep-2006 | 2,073 | 1,469 | 453 | 151 | 324 | 231 | 1,518 |
Switzerland | Sep-2005 | 403 | 373 | 30 | — | 160 | 2 | 241 |
| Dec-2005 | 585 | 577 | 8 | — | 353 | 1 | 231 |
| Mar-2006 | 903 | 824 | 79 | — | 654 | — | 249 |
| Jun-2006 | 1,209 | 860 | 349 | — | 568 | 2 | 639 |
| Sep-2006 | 1,742 | 1,448 | 293 | — | 790 | — | 951 |
Statement VII: Residual Maturity
and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International |
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS
Statements) - Amount outstanding as at | end
of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Concld.) |
(Rs. crore) |
Country of Transacting | Period | Total | Residual
Maturity | Sector |
Units | | | | International | Short | Long | Un- | Bank | Non-Bank | Non-Bank |
| | | | | Claims | Term | Term | allocated | | Public | Private |
Turkey | | | Sep-2005 | 376 | 376 | — | — | 31 | — | 345 |
| | | | Dec-2005 | 559 | 558 | 1 | — | 44 | — | 514 |
| | | | Mar-2006 | 568 | 566 | 2 | — | 67 | — | 501 |
| | | | Jun-2006 | 764 | 447 | 318 | — | 174 | — | 591 |
| | | | Sep-2006 | 1,211 | 1,164 | 48 | — | 656 | — | 555 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
United Arab Emirates | Sep-2005 | 3,402 | 2,736 | 666 | — | 294 | 6 | 3,102 |
| | | | Dec-2005 | 4,505 | 3,344 | 1,161 | — | 1,004 | — | 3,500 |
| | | | Mar-2006 | 4,059 | 2,824 | 1,236 | — | 1,043 | — | 3,016 |
| | | | Jun-2006 | 3,824 | 2,257 | 1,567 | — | 774 | 1 | 3,050 |
| | | | Sep-2006 | 5,100 | 3,011 | 2,090 | — | 640 | 1 | 4,460 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
United Kingdom | Sep-2005 | 10,133 | 6,901 | 2,919 | 313 | 5,989 | 24 | 4,120 |
| | | | Dec-2005 | 12,827 | 9,535 | 3,142 | 150 | 9,818 | 18 | 2,991 |
| | | | Mar-2006 | 14,212 | 10,798 | 3,286 | 128 | 10,688 | 21 | 3,504 |
| | | | Jun-2006 | 12,106 | 7,201 | 4,278 | 627 | 7,221 | 30 | 4,856 |
| | | | Sep-2006 | 16,745 | 11,392 | 4,948 | 405 | 10,410 | 29 | 6,306 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
United States | Sep-2005 | 18,409 | 15,618 | 2,612 | 179 | 8,048 | 257 | 10,103 |
| | | | Dec-2005 | 24,471 | 20,590 | 3,664 | 217 | 11,544 | 444 | 12,483 |
| | | | Mar-2006 | 23,176 | 18,664 | 4,409 | 103 | 8,963 | 513 | 13,700 |
| | | | Jun-2006 | 24,283 | 18,388 | 5,736 | 159 | 7,757 | 446 | 16,080 |
| | | | Sep-2006 | 29,152 | 22,701 | 6,451 | — | 10,916 | 359 | 17,877 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
No Specific Country | Sep-2005 | 1,217 | 1,186 | 30 | — | 709 | — | 508 |
| | | | Dec-2005 | 1,096 | 1,047 | 49 | — | 375 | — | 720 |
| | | | Mar-2006 | 2,567 | 1,727 | 840 | — | 21 | — | 2,545 |
| | | | Jun-2006 | 2,362 | 1,557 | 806 | — | 21 | 4 | 2,337 |
| | | | Sep-2006 | 1,926 | 1,541 | 385 | — | 22 | — | 1,904 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
@ : Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and
Jersey. #: Includes Miday Island and Wake Islands.
— : Nil/Negligible.
Notes :
1. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
2. Residual maturity
“Unallocated” comprises maturity not applicable (e.g., for equities)
and
Maturity information not available.
3. “No Specific Country”
means the Country Information has not been provided by the Reporting Bank
branches.
4. Data have been revised for previous quarters. | |